Figure 4: Loss of KMT5C confers resistance to erlotinib and osimertinib in EGFR mutant cell lines.
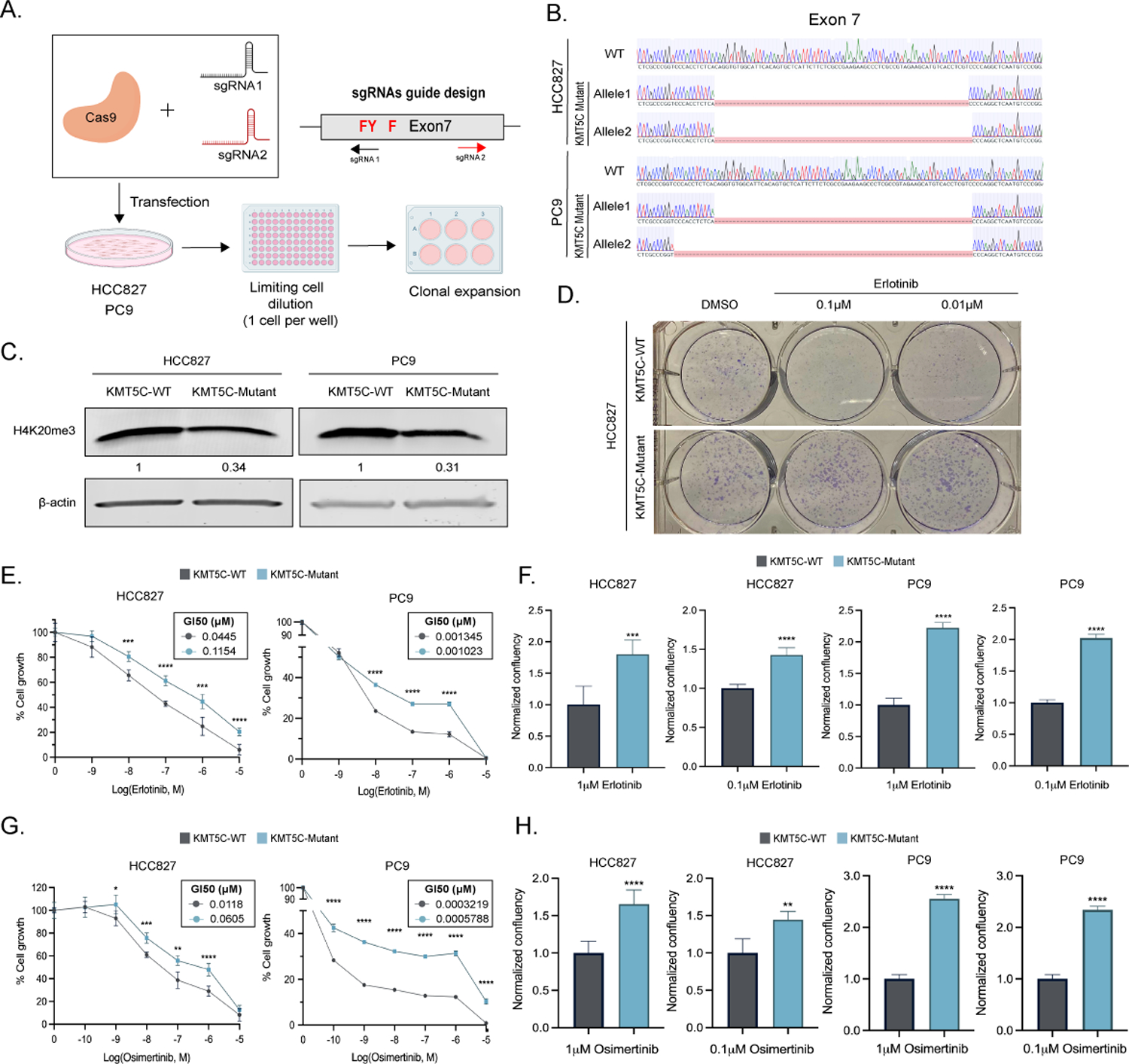
A) CRISPR Cas9 strategy to generate KMT5C SET domain mutants. SET domain active site residues are in red. B) Alignment of exon 7 sequence in WT and mutant clones using benchling (Sequence Alignment Tool, 2021) retrieved from https://benchling.com. B) Representative western blot of H4K20me3 from WT and mutant HCC827 and PC9 clones. β-actin serves as a loading control. D) Clonogenic assay in HCC827 KMT5C mutant and WT cells in the presence of 0.1 or 0.01μM erlotinib containing media for 8 days. Erlotinib E) or Osimertinib G) dose response curves following exposing the indicated cells to varying concentrations of erlotinib containing media for 72 hours. Cell confluency of KMT5C mutant cells was compared to KMT5C WT cells in the presence of 1 or 0.1μM F) erlotinib or H) osimertinib for 72h. Data relative to respective normalized DMSO control treatments is represented. Welch’s t-test was used to evaluate statistical significance.
