Fig. 5.
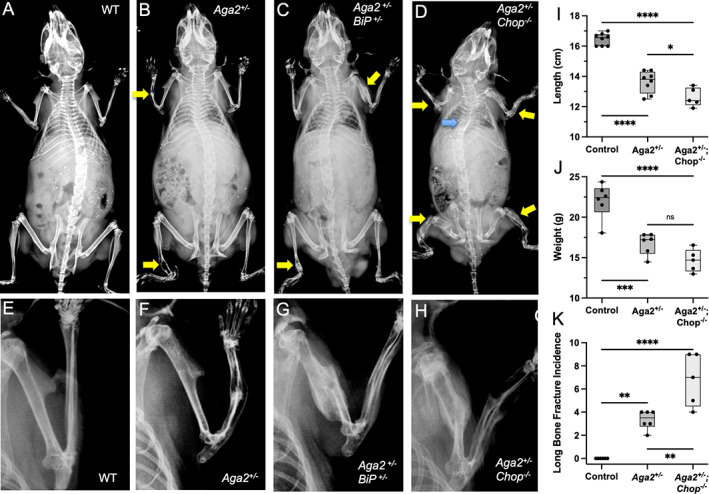
Genetic deletion of CHOP results in increased bone fragility and impaired bone development. (A–H) X‐ray images of WT, Aga2 +/−, Aga2 +/− ;BiP +/− , and Aga2 +/− ;Chop −/− male 2‐month‐old mice with insets showing closer imaging of forearm. Yellow arrows point to long‐bone fractures, blue arrow points to kyphoscoliosis. (I–K) Quantification of body length, body weight, and fracture incidence in WT (n = 6), Aga2 +/− (n = 6), and Aga +/− ;Chop −/− (n = 6) male mice. Bars represent median and interquartile range. Two‐way ANOVAs were performed, *p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant.
