Fig. 1.
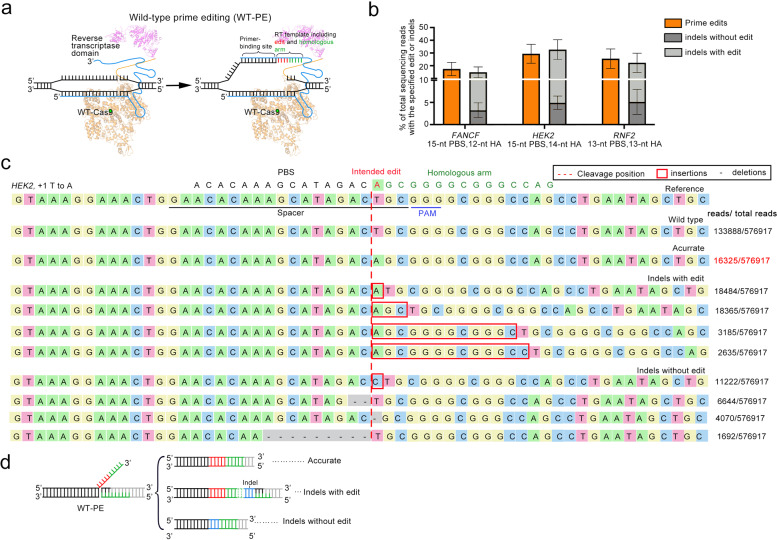
Design and characterization of WT-PE. a A diagram showing the putative action mode of WT-PE. Different from PE2, WT-PE uses a nuclease preserved spCas9 and introduces DSB in the target site (left panel). The broken non-target strand is then recognized by PBS of the pegRNA and then extended by RT domain in the guidance of RT template. The RT template is designed to contain aimed edit (in red) and a homologous arm (HA, in green) that is complementary to the PAM proximal end of the target strand (right panel). b HTS analysis of the editing outcomes of WT-PE. Three types of outcomes were observed through the HTS: accurate edits, edits containing indels and pure indels. The prime edits represented accurate edits+edits containing indels. Plots showed mean ± s.d. of three independent biological replicates. c Sequence alignment showing top 10 sequences of WT-PE outcomes in HEK2 locus. Desired sequence containing +1 A to T conversion served as a reference sequence with spacer and PAM sequences underlined. The position of DSB was labeled with a red dash. d Schematic diagram of three types of outcomes.