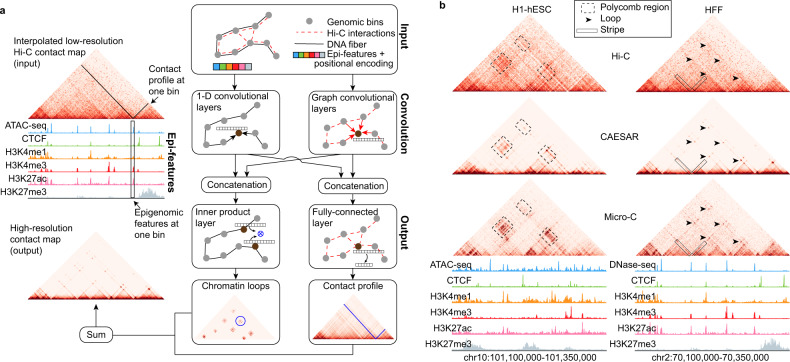
Fig. 1. Overview of the model.
a Model architecture. The model inputs are a Hi-C contact map and a number of epigenomic features including histone modifications, chromatin accessibility, and protein binding profiles. The lower-resolution Hi-C contact map is first interpolated into a 200 bp resolution contact map, and then transformed into a graph in which the nodes represent 200-bp genomic bins and the edges represent the interpolated contacts between the nodes. Positional encoding is unrelated to Hi-C or epigenomic data and only encodes node order in the genome. The epigenomic features and positional encoding are assigned to the corresponding nodes as node attributes. The inputs are fed into 1D convolutional and graph convolutional layers to generate hidden representations, which extract features from both nearby genomic regions along the 1D DNA sequence and spatially contacting regions specified by . The output layers take input the hidden representations and predict the contact profile at each 200-bp bin as well as the chromatin contacts between bins. b In an example region, the polycomb interactions are accurately predicted by CAESAR. In another example region, loops and stripes undetected by Hi-C are accurately predicted by CAESAR.