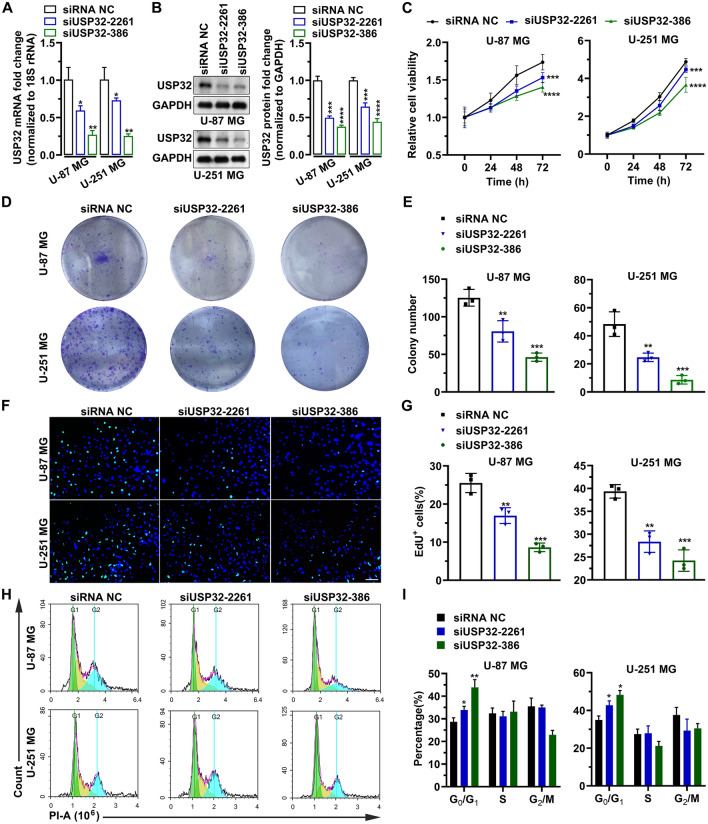
Figure 3.
Knockdown of USP32 inhibits cell growth. (A) The mRNA level of USP32 was reduced by siUSP32-2261 and siUSP32-386. Data are represented as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. (B) Left panel: Representative images of three independent western bolting analyses showing the knockdown efficiency of siUSP32-2261 and siUSP32-386. Right panel: statistical quantification of left panel. (C) MTT assay determining the cell viability of U-87 MG and U-251 MG. Data are represented as mean ± SD of six biological replicates. (D) Representative images of three independent colony formation assays showing that USP32 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation. (E) Statistical quantification of (D). (F) USP32 knockdown reduced the number of EdU+ cells. Bar: 10 μm. (G) Statistical quantification of (F). Data are represented as mean ± SD of three technical replicates. (H) Representative images of three independent cell cycle assays by flow cytometry. (I) Histogram showing the percentage of each cell-cycle phase in (H). One way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test: vs siRNA NC, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.