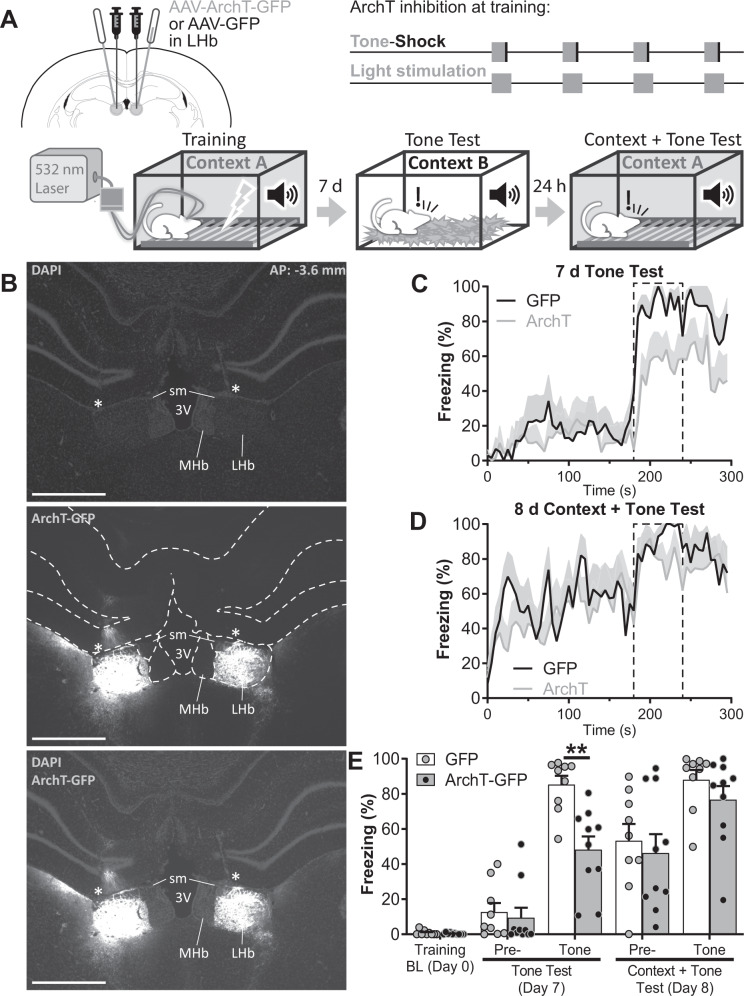
Fig. 4. Optogenetic inactivation of the LHb during cue and US, impaired cued but not contextual FC.
A Experiment diagram: Top-Left: animals were bilaterally transfected with AAV-ArchT-GFP or AAV-GFP in the LHb and implanted with optic fibers above the LHb 4 weeks before training. Top-Right: during training, optogenetic light stimulation was delivered starting with the tone and stopping 5 s after the shock (tone and shock presentations were as previously described for cued FC). Bottom: diagram of training and memory tests. Cued memory was tested 7 days after training in Context B. The same animals were re-tested the following day in the training context to evaluate contextual FC memory and tone freezing in context + tone condition. B Microphotographs of the AAV-ArchT-GFP infection at ~3.6 mm posterior to Bregma (top, middle, bottom: DAPI, GFP, and merge respectively). Dashed white lines in the middle panel delimitates brain structures. * indicates the optic fiber tract. MHb: medial habenula, sm: stria medullaris, 3V: third ventricle. Scale bars: 1 mm. Freezing over time during tone test at day 7 (C) and during context + tone test at day 8 (D). Dashed line delimits tone presentation. E Average freezing on tone test, and context + tone test sessions. During tone test ArchT group displayed lower levels of freezing to the tone than GFP group (t(66) = 3.410, p = 0.0078). The following day, during context + tone session, freezing levels of the ArchT group to both the context and the tone were equivalent to those of the GFP group (t(66) = 0.178, p = 1.0000 and t(66) = 1.145, p = 0.8742 respectively; nGFP = 9, nArchT = 10). Additional statistics can be found in the Statistics details section of Supplementary Material.