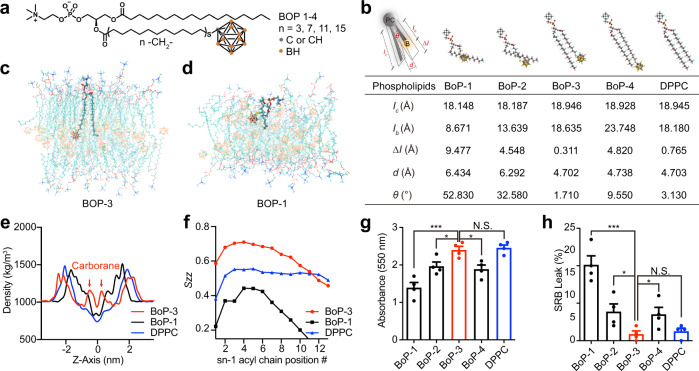
Fig. 2. Boronated phospholipids (BoPs) with hydrophobic tails of matched length show superior self-assembly and packing properties.
a Chemical structure of BoPs with different lengths of alkyl chain. b Spatial configuration and structural parameters of corresponding BoPs. Ic, carbon arm length (Å); Ib, boron arm length (Å); Δl, length difference between lipid arms (Å); d, distance between lipid arms (Å); θ, dihedral angle between lipid arms (°). c Cross-sectional area of bilayers formed from BoP-3 and Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) in a 10 ns, 128 monomer MD simulation. Lipids are depicted in wireframe format. d Cross-sectional area of bilayers formed from BoP-1 and DPPC in a 10 ns, 128 monomer MD simulation. Lipids are depicted in wireframe format. e BoPs and DPPC density (excluding water contribution) post 10 ns MD simulation. f Chain order parameter (SZZ) for BoPs following 10 ns MD simulation. SZZ indicates order of lipid chain with respect to bilayer normal vector. Error bars show range for last two adjacent 10 ns block means. g Encapsulation of SRB (n = 4) by various BoPs and DPPC under same conditions. ***p = 0.0010, BoP-2 vs BoP-3: *p = 0.0264, BoP-4 vs BoP-3: *p = 0.0126. h Release of SRB from boronsomes (n = 4) with various BoPs and DPPC in 50% bovine serum at 37 °C after 24 h. ***p = 0.0003, BoP-2 vs BoP-3: *p = 0.0358, BoP-4 vs BoP-3: *p = 0.0433. Three independent experiments were performed and representative results are shown. N.S., no significant difference, data are shown as mean ± SEM, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.