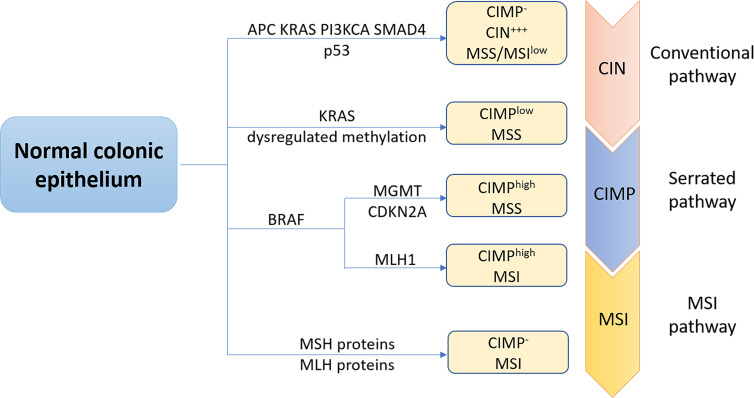
Figure 1.
The three major molecular pathways of colorectal cancer. The conventional chromosomal instability (CIN) pathway, initiated by APC mutation, then followed by mutations in KRAS, PIK3CA and SMAD4, loss of heterozygosity of p53 mutation was observed in most CRC cases. CRC progress and development via this pathway is often associated with no or low levels of the CpG island methylation pathway (CIMP- ), high levels of CIN (CIW+++), and microsatellite stability (MSS). Approximately one third CRC cases is regulated through the serrated pathway, which can be subdivided into CIMPlow MSS tumors with KRAS mutations, BRAF mutant CIMPhigh MSS tumors or BRAF mutant CIMPhigh microsatellite instability (MSI) tumors. Serrated pathway is commonly associated with silencing of 0-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A) or MLHl. MSI pathway is a third important pathway of CRC caused by dysfunction of DNA mismatch repair genes, encoding Mutl homolog (MLH) or MutS homolog (MSH) proteins.