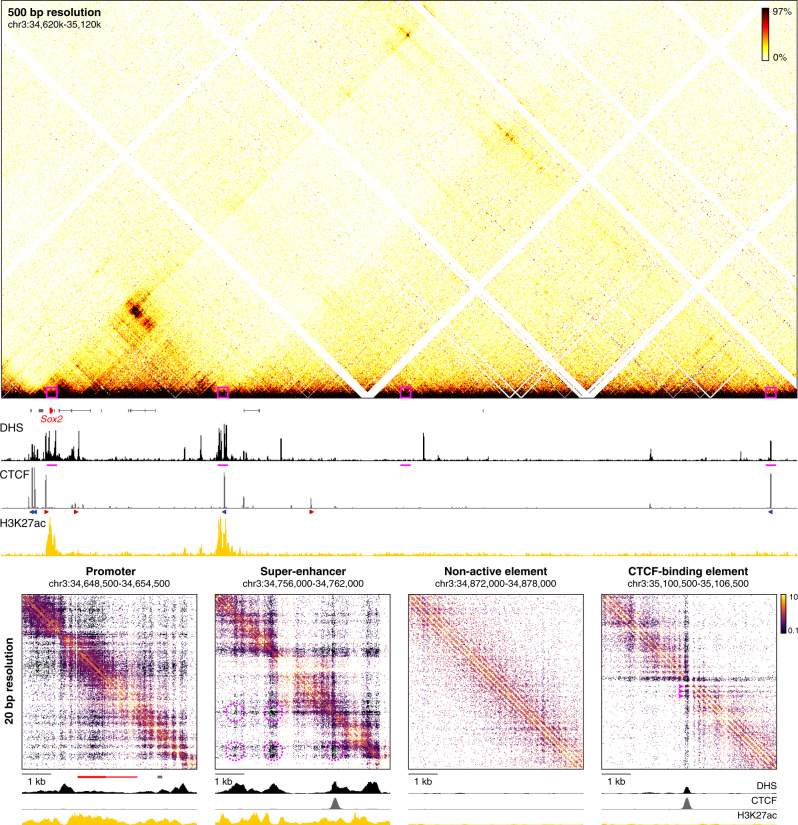
Fig. 2. High-resolution analysis of Tiled-MCC ligation junctions identifies micro-topologies of cis-regulatory elements in the Sox2 locus.
The fine-scale contact matrices at the bottom show ligation junctions identified by Tiled-MCC in the Sox2 locus at 20 bp resolution. A large-scale contact matrix (500 bp resolution), gene annotation (Sox2 in red, coding genes in black, non-coding genes in gray), DNase hypersensitive sites (DHS), and ChIP-seq data for CTCF and H3K27ac for the extended Sox2 locus are shown in the top panels. The 6 kb regions covered in the fine-scale contact matrices are highlighted with magenta boxes in the contact matrix at the top and with magenta bars below the top DHS profile, and show a promoter, super-enhancer, non-active element, and CTCF-binding element. The axes of the top and bottom DHS and ChIP-seq profiles for CTCF and H3K27ac are fixed and have the following ranges: DHS = 0–5; CTCF = 0–1500; H3K27ac = 0–50. The orientations of CTCF motifs at prominent CTCF-binding sites are indicated by arrowheads (forward orientation in red; reverse orientation in blue). The magenta highlights in the contact matrix covering the super-enhancer indicate enriched interactions between DHSs; the magenta highlights in the contact matrix covering the CTCF-binding element indicate phased nucleosomes.