Figure 1. GLUT3 is required for the effector function of Th17 cells.
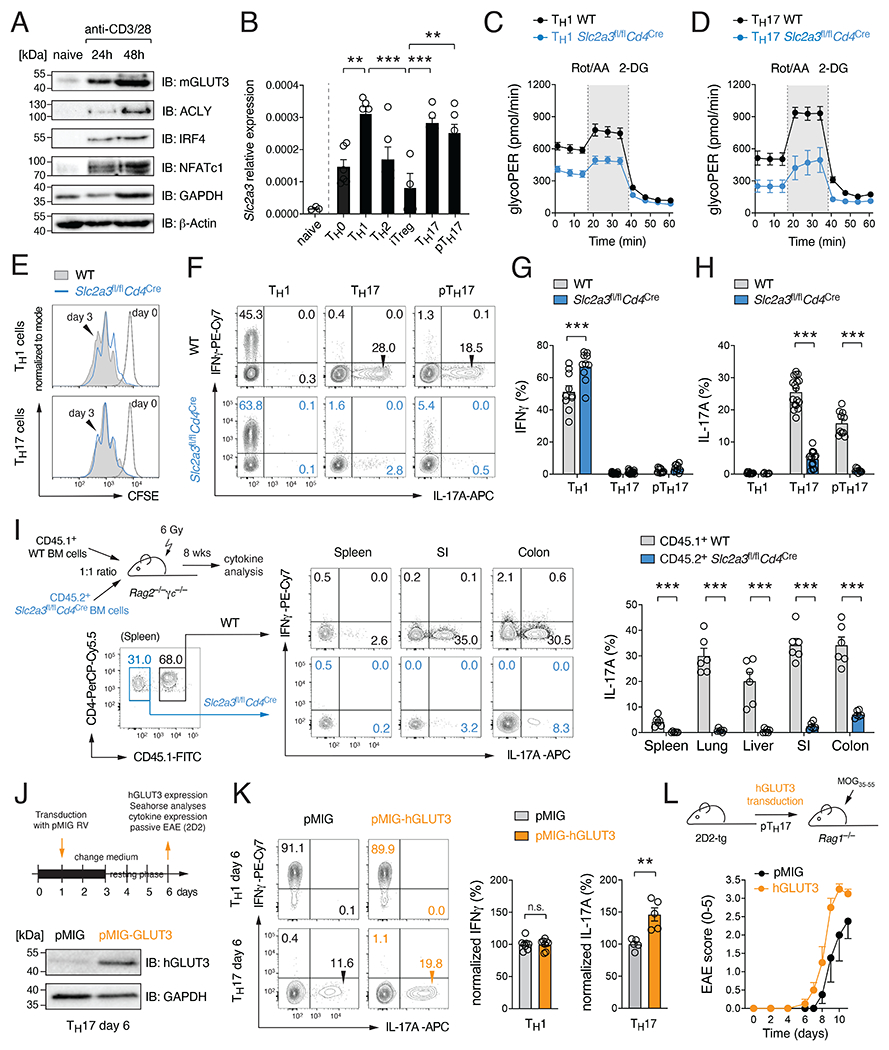
(A) Immunoblot analysis of murine GLUT3, ACLY, IRF4, NFATc1 and GAPDH expression. (B) Analysis of Slc2a3 (GLUT3) gene expression in naïve CD4+ T cells and T helper (Th) cell subsets by qRT-PCR; means ± SEM of 5-6 mice. (C and D) Glycolytic proton efflux rate (glycoPER) analyses of WT and GLUT3-deficient Th1 (C) and Th17 (D) cells using a Seahorse extracellular flux analyzer; means ± SEM of 5 mice. (E) Proliferation analysis of WT and GLUT3-deficient Th1 and Th17 cells. (F-H) Flow cytometric analysis of IFNγ (G) and IL-17 (H) production of WT and GLUT3-deficient Th1, Th17 and pathogenic Th17 (pTh17) cells after re-stimulation with PMA/Iono for 5 h; means ± SEM of 9-15 mice. (I) Generation of mixed BM chimeras using BM from CD45.2+ Slc2a3fl/flCd4Cre and CD45.1+ WT mice at a 1:1 ratio. 8 weeks after reconstitution, the production of IFNγ and IL-17 in CD4+ T cells of WT and GLUT3-deficient BM origin was analyzed; means ± SEM of 6 mice. (J-L) Ectopic expression of GLUT3 in T cells augments Th17 cell effector function. (J) Retroviral transduction of WT T cells with GLUT3 or empty control vectors (EV). Immunoblot analysis of GLUT3 overexpression. (K) Flow cytometric analysis of IFNγ and IL-17 production of GLUT3-transduced Th1 and Th17 cells; means ± SEM of 5-8 mice. (L) Clinical EAE scoring of Rag1−/− mice after transfer of GLUT3-transduced 2D2 T cells; means ± SEM of 4 mice per cohort. **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.001 by unpaired Student’s t-test (B), (G-I) and (K); n.s., non-significant.
