Figure 2. Ablation of GLUT3 in T cells prevents autoimmunity.
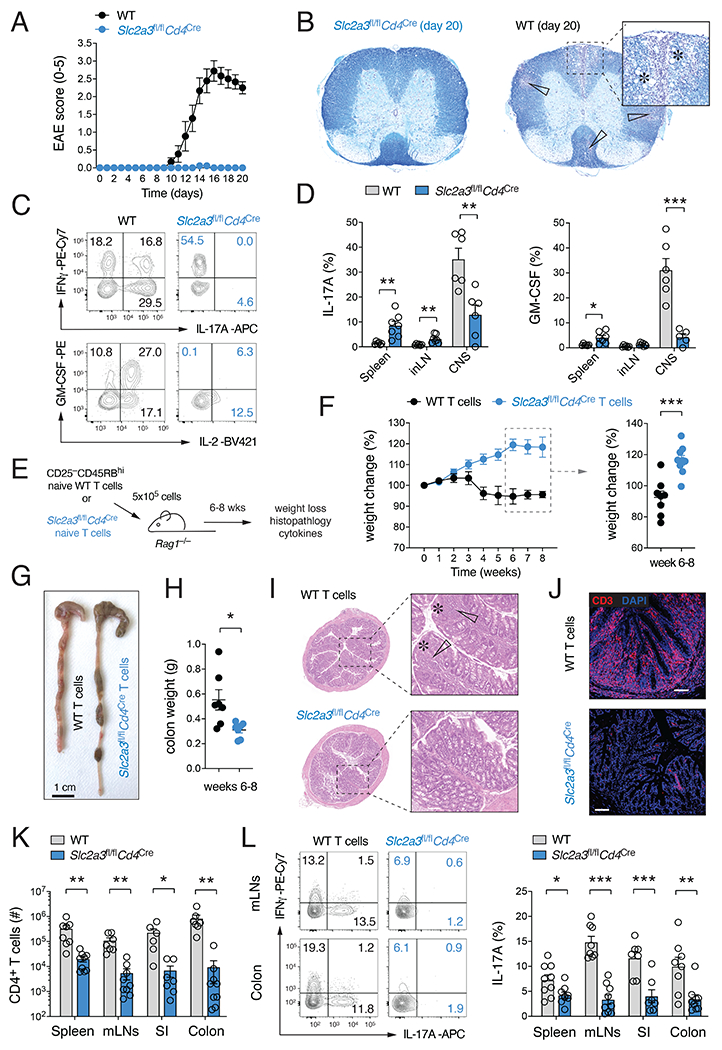
(A-D) Slc2a3fl/flCd4Cre mice are protected from experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). (A) Clinical EAE scores of WT and Slc2a3fl/flCd4Cre mice after immunization with MOG35-55 peptide emulsified in CFA; means ± SEM of 9 mice per cohort. (B) Representative histopathological examination of spinal cord sections of WT and Slc2a3fl/flCd4Cre mice 20 days after MOG35-55 peptide immunization. White arrows and asterisks indicate leukocytic infiltrates and areas of demyelination, respectively. (C and D) Frequencies of IL-17 and GM-CSF-producing CD4+ T cells in the spleen, inLNs and CNS of WT and Slc2a3fl/flCd4Cre mice; means ± SEM of 6-7 mice. (E-L) GLUT3-deficient T cells fail to induce adoptive transfer autoimmune colitis. (F) Weight loss of Rag1−/− host mice after transfer of naive CD4+ T cells from WT or Slc2a3fl/flCd4Cre mice; means ± SEM of 8-9 host mice. (G and H) Representative macroscopic pictures (G) and colon weights (H) 8 weeks after T cell transfer; means ± SEM of 6-7 recipient mice. (I and J) Representative H&E-stained colon sections (I) and anti-CD3 immunofluorescence analysis of inflammatory tissue damage and T cell infiltration (J). (K) T cell numbers in the spleen, mLNs, small intestine (SI) and colon in Rag1−/− recipient mice 6 to 8 weeks after transfer of T cells; means ± SEM of 6-9 host mice. (L) IFNγand IL-17 cytokine production of WT and GLUT3-deficient T cells in the spleen, mLNs, SI and colon 6-8 weeks after T cell transfer; means ± SEM of 7-9 mice. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.001 by unpaired Student’s t-test (D), (F), (H) and (K,L).
