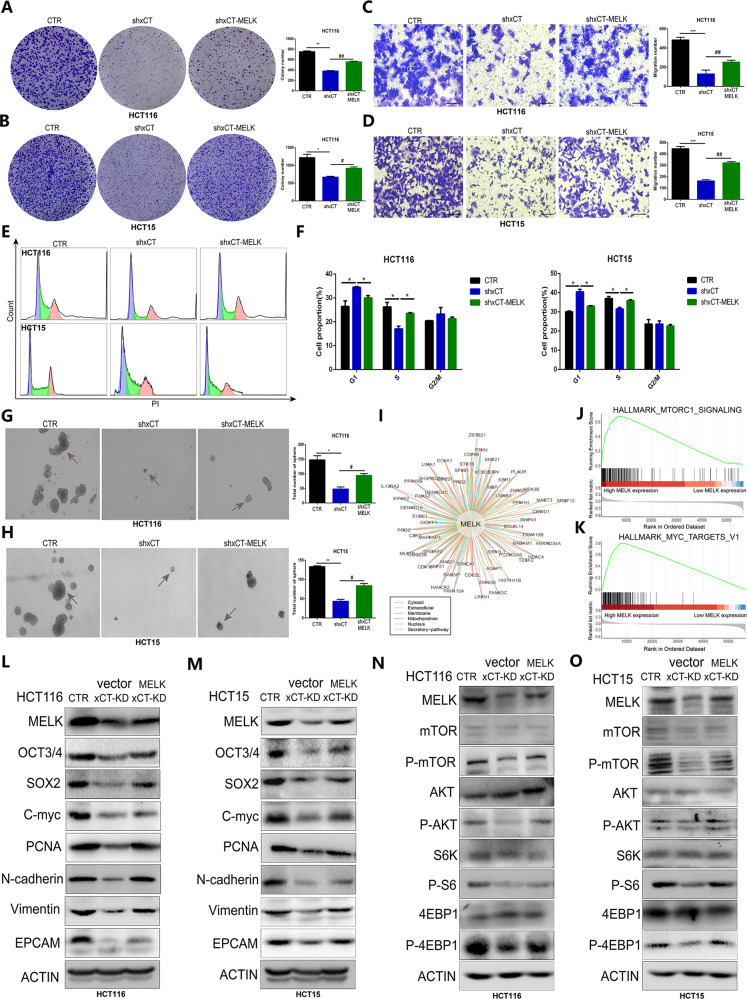
Fig. 8. MELK is required for xCT-mediated CRC tumorigenesis and AKT/mTOR signaling.
A, B The colony formation assay showed that the suppressive effect of xCT inhibition on the proliferation of CRC cells was reversed by MELK upregulation. C, D Transwell assays indicated that MELK overexpression effectively recovered the migration capability inhibited by xCT knockdown in CRC cells. E, F Cell cycle assay confirmed that MELK rescued the suppression of xCT inhibition on G1/S transition. G, H The sphere formation assay indicated that upregulated MELK rescued the suppressive effect of xCT inhibition on the sphere-forming capability of CRC cells. I The interaction of MELK with different factors expressed in various organelles. J, K GSEA indicated that upregulated expression of MELK was closely related to the activation of signaling pathways, including hallmark_mTORC1_signaling and hallmark_MYC_targets_V1. L, M Western blot analysis confirmed that upregulated MELK rescued the suppression of the expression of tumorigenesis- and stemness-related factors in CRC cells with xCT knockdown. N, O The suppressive effect of xCT knockdown on the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway was rescued by MELK overexpression. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01.