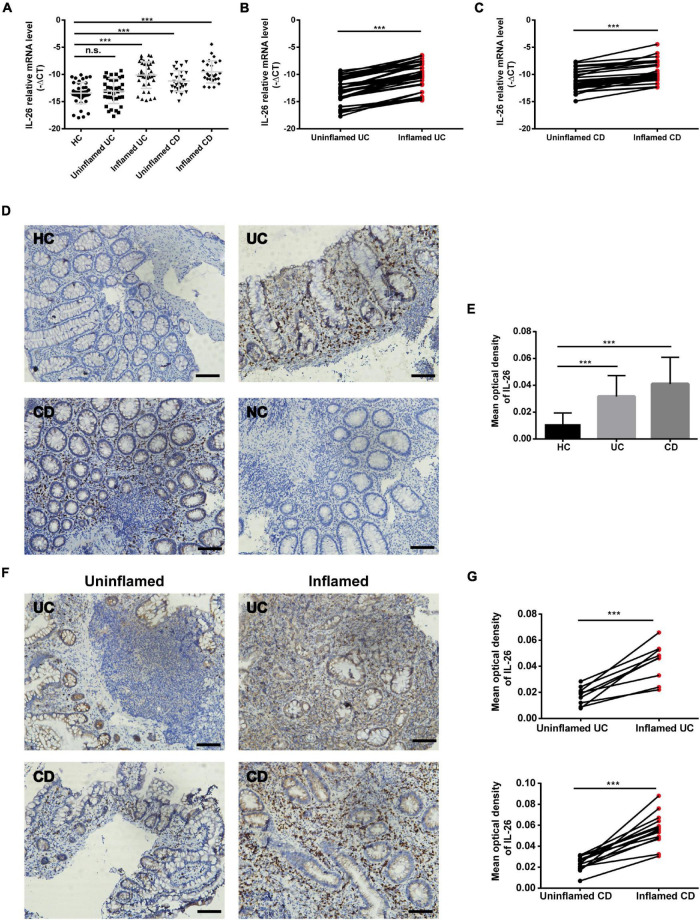
FIGURE 1.
IL-26 expression is increased in the inflamed intestinal mucosa of IBD patients. (A) IL-26 mRNA levels in inflamed and uninflamed intestinal mucosa from UC patients (n = 37) and CD patients (n = 26), and normal intestinal mucosa from healthy controls (HC) (n = 45). (B,C) IL-26 mRNA levels in paired inflamed and uninflamed intestinal mucosa from patients with UC (n = 37) (B) and patients with CD (n = 26) (C). (D) Immunohistochemical staining for IL-26 in intestinal mucosa from patients with UC and CD, and HC. Negative control (NC): omission of the primary antibody. Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) The semi-quantitative analysis of immunohistochemistry staining of IL-26 in intestinal mucosa from patients with UC (n = 22) and CD (n = 28), and HC (n = 23). (F) Immunohistochemical staining for IL-26 in paired inflamed and uninflamed intestinal mucosa from the same UC and CD patients. Scale bar, 100 μm. (G) The semi-quantitative analysis of immunohistochemistry staining of IL-26 in paired inflamed and uninflamed intestinal mucosa from the same UC and CD patients. ***P < 0.001. n.s., not significant.