Figure 5.
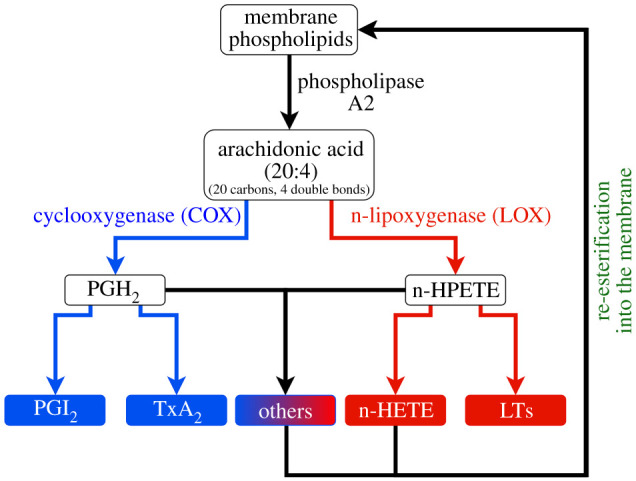
The typical oxylipin and enzymatically oxidized phospholipid pathway in circulating blood cells. Membrane phospholipids can be cleaved by phospholipase A2 (PLA2) into polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as arachidonic acid (FA 20:4). These PUFAs are oxygenated via the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) or lipoxygenase (LOX) enzymes to generate oxylipins, which are referred to as ‘eicosanoids’ if generated from 20-carbon PUFAs such as arachidonic acid (AA). Some oxylipins may be re-esterified back to the membrane to form enzymatically oxidized phospholipids. The ‘n-’ prefix denotes the enzyme isoforms which are responsible for generating oxylipin positional isomers at the corresponding ‘n-’ carbon on AA (e.g. 12-LOX in platelets generating 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, or 12-HETE). HPETE, hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid; LT, leukotriene.
