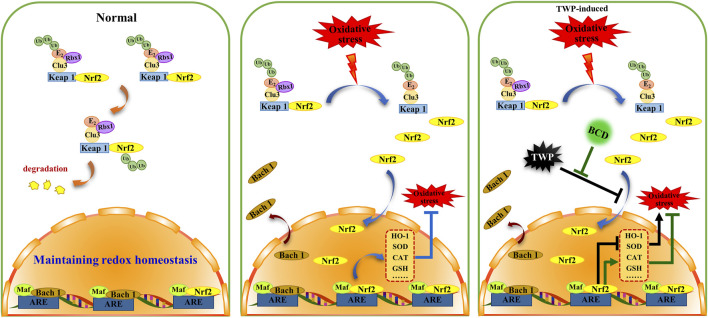
FIGURE 9.
The proposed schema for BCD function in oxidative stress of TWP-induced POI. BCD prevents TWP-induced oxidative stress through regulating Nrf2/Keap 1 signaling pathway. In normal circumstances, Nrf2 is predominantly distributed in the cytoplasm, where it incorporated into a complex that binds to Keap 1 and Clu3, and then to be degradation (orange indicator). While, Bach 1 is mainly distributed in nucleus. When oxidative stress occurs, Nrf2 releases from Nrf2-Keap1-Cul3 complex, then translocates into the nucleus to combined with Maf-ARE, and subsequently promotes expressions of antioxidant enzymes, that included HO-1, SOD, CAT (blue indicator). Exposure to TWP induces ovarian oxidative stress, furthermore, TWP blocks nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and Bach 1 which ultimately inhibits the expression of antioxidant enzymes resulting in aggravation of oxidative damage (black indicator). However, with BCD co-treatment, the blocking of Nrf2 and Bach 1 nuclear translocation were reversed and the expression of antioxidant enzymes were increased (green indicator).