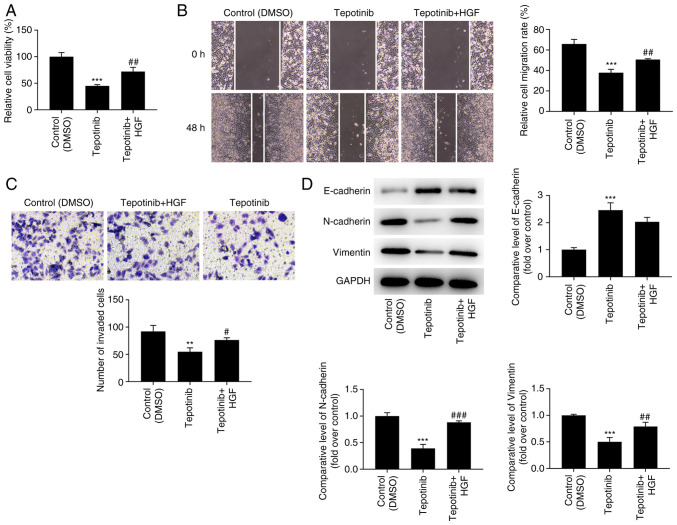
Figure 6.
Tepotinib inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of WM451 cells by restraining the activation of MET and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. (A) The proliferation of WM451 cells treated with or without 10 ng/ml tepotinib and 50 ng/ml HGF was detected using the MTT assay. (B) The migratory activity of WM451 cells treated with or without 10 ng/ml tepotinib and 50 ng/ml HGF was assessed using the wound healing assay. Magnification, ×100. (C) The invasive activity of WM451 cells treated with or without 10 ng/ml tepotinib and 50 ng/ml HGF was detected using the Transwell assay. Magnification, ×100. (D) The expression levels of the EMT-related proteins in WM451 cells treated with or without 10 ng/ml tepotinib and 50 ng/ml HGF were detected using western blot analysis. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. control (DMSO) group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 vs. tepotinib. MET, MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor.