Fig. 5.
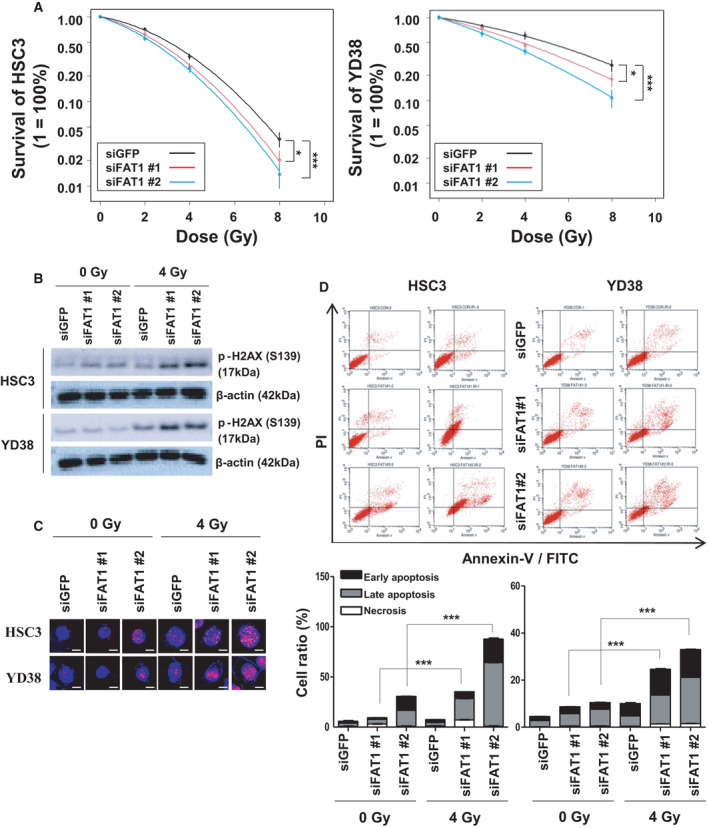
FAT1 is a crucial factor that regulates the sensitivity of radiotherapy in HNSCC. (A) The radiation susceptibility was estimated using a CFA. Colony formation occurred in the siGFP‐, siFAT1 #1‐, or siFAT1 #2‐transfected HSC3 (left) and YD38 (right) cells under radiation doses of 0, 2, 4, and 8 Gy. All experiments were performed in triplicate. The two‐way ANOVA test was used to estimate the P value. (HSC3; *P = 0.0193, ***P = 4.77 × 10−5 vs. siGFP, YD38; *P = 0.0422, ***P = 0.0003 vs. siGFP). (B) DNA damage to HNSCC cell lines upon radiation exposure was evaluated in terms of level and foci formation of γ‐H2AX (pS139). γ‐H2AX (S139) protein levels in the siGFP‐, siFAT1 #1‐, or siFAT1 #2‐transfected HSC3 and YD38 cells exposed to radiation treatment of 0 or 4 Gy were determined using western blot. β‐Actin was included as an internal loading control. (C) γ‐H2AX foci formation in the same condition was measured using ICC. The cells were stained for γ‐H2AX (green), DNA (blue; DAPI) and observed using confocal microscopy (scale bar: 10 μm). (D) Cell apoptosis was determined by means of Annexin V‐FITC/PI staining using flow cytometry. The siGFP‐, siFAT1 #1‐, or siFAT1 #2‐transfected HSC3 and YD38 cells exposed to radiation treatment of 0 or 4 Gy were analyzed with an Annexin V‐FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit. Cells were classified as healthy (Annexin V−, PI−), early apoptotic (Annexin V+, PI−), late apoptotic (Annexin V+, PI+), and necrotic (Annexin V−, PI+) (upper) cells. Cell death ratio was calculated as a sum of early apoptosis, late apoptosis, and necrosis percentages. All experiments were performed in triplicate. The t‐test was used to estimate the P value. (HSC3 in IR 4 Gy; siFATI1 #1 ***P = 7.37 × 10−7, siFAT1 #2 ***P = 2.82 × 10−6 vs. IR 0 Gy, YD38 in IR 4 Gy; siFATI1 #1 ***P = 2.29 × 10−6, siFAT1 #2 ***P = 9.62 x 10−7 vs. IR 0 Gy). All data have been represented as mean ± SD. The number of asterisks denote the level of statistical significance: *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; GFP, green fluorescent protein; PI, propidium iodide; DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole.
