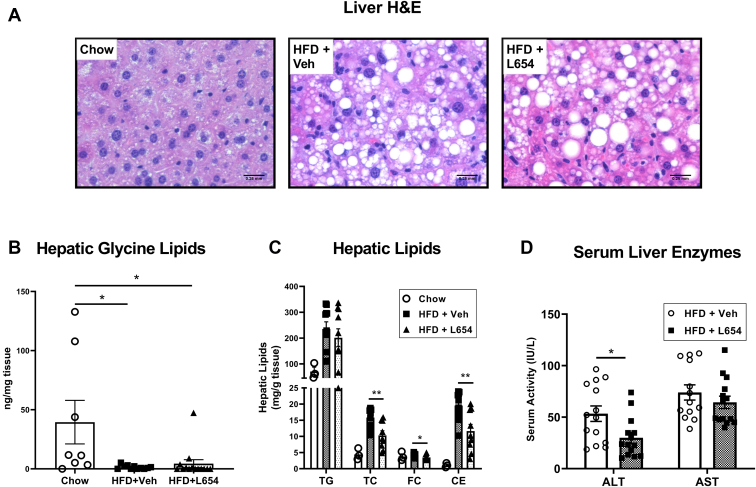
Fig. 2.
L654-injected Ldlr−/− mice have lower hepatic cholesterol and serum ALT. Ldlr−/− mice were fed either standard low-fat chow diet (Chow) or Western-type HFD for 14 weeks. Mice fed HFD were intraperitoneally injected with L654 (1 μg) (HFD + L654) or vehicle (HFD + Veh) every 48 h during the final 7 weeks of HFD. Livers were formalin-fixed, sectioned, and H&E stained (A) for visualizing hepatic steatosis (200×). Lipids were extracted from livers using Bligh and Dyer method, and total bacterial glycine lipids (B) were quantified by UPLC-MS/MS (n = 8–14, mean ± SEM). Liver lipids were extracted from HFD-fed mice using a modified Folch extraction and measured by enzymatic methods (C), (TG; total cholesterol [TC]; free cholesterol [FC]; cholesteryl ester [CE]) (n = 3–10, mean ± SEM). The activity of serum liver enzymes, ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), is shown (D) (n = 15, mean ± SEM). Statistical significance determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test (∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01).