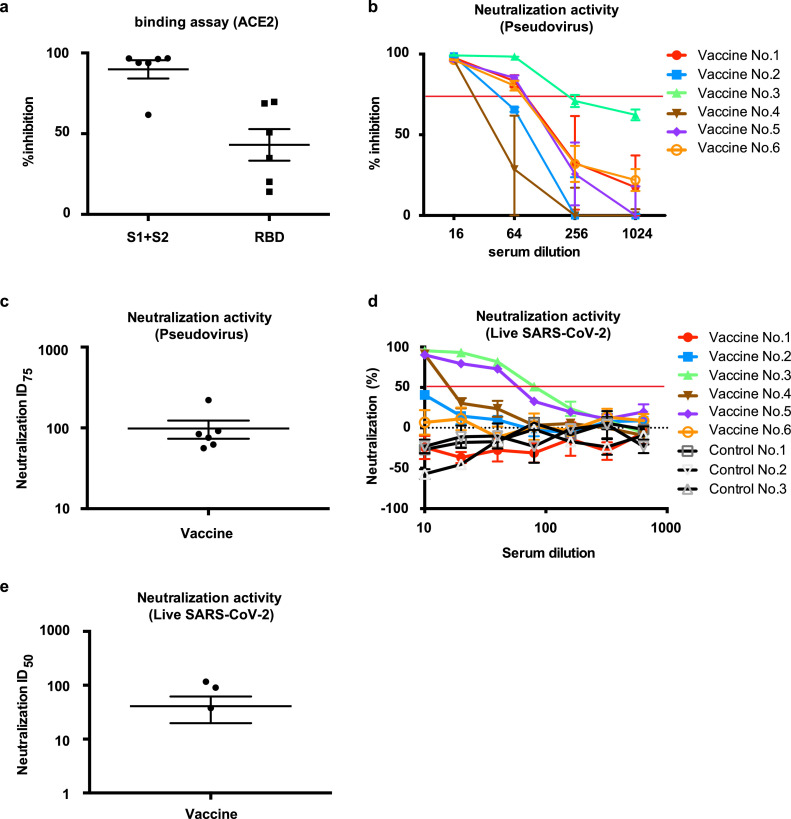
Fig. 4.
Neutralizing activity of DNA vaccine-induced antibodies. (a) Inhibitory activity of vaccine-induced antibodies for the binding of ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 Spike or RBD. The vaccinated sera at 8 weeks after 1st vaccination was used at 10-fold dilution for ELISA. “S1+S2” indicates the binding between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 Spike. “RDB” indicates the binding between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 RBD. (b) Dose-dependent pseudovirus neutralizing activity of vaccine-induced antibodies. Serial dilution (x16, x64, x256, and x1024) of vaccinated sera at 8 weeks after 1st vaccination was analyzed. The horizontal red line indicates 75% inhibition. Individual vaccinated rats were shown. (c) ID75 titers for pseudovirus neutralization activity of sera collected at 8 weeks after 1st vaccination from (b). (d) Dose-dependent live SARS-CoV-2 neutralization activity of vaccine-induced antibodies, analyzed by focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT). Serial dilution (x10, x20, x40, x80, x160, x320, and x640) of vaccinated sera at 8 weeks after 1st vaccination. The horizontal red line indicates 50% inhibition. Individual vaccinated rats were shown, (e) ID50 titers for live SARS-CoV-2 neutralization activity of sera collected at 8 weeks after 1st vaccination from (d). Vaccine No.3 and Control No.3: 7 weeks sample. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. See also Fig. S5 and S6. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)