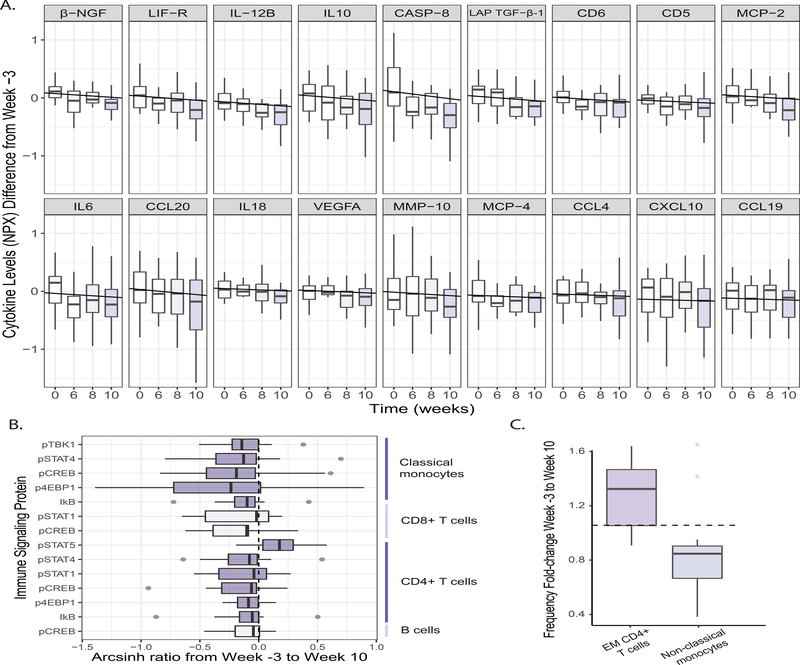
Figure 6. Fermented food consumption decreases levels of inflammation.
(A) Cytokines, chemokines, and other serum proteins plotted that change significantly from baseline (week −3) to end of intervention (week 10) (SAM two-class paired, FDR ≤ 0.05, q-value ≤ 0.1). Negative correlations for levels of each analyte across time calculated using LME. NPX refers to the normalized protein expression used by Olink Proteomics’ log2 scale. Fgf-21 also significantly decreased across time (data not shown).
(B) Cell type-specific endogenous signaling proteins, measured using CyTOF, that change significantly from baseline (week −3) to end of intervention (week 10) (SAM two-class paired, FDR < 10%). Arcsinh ratio plotted from week −3 to week 10.
(C) Fold change of cell frequencies (calculated as percentage of CD45+ cells) that change significantly from baseline (week −3) to end of intervention (week 10) (Wilcoxon paired test, adjusted p-value ≤ 0.05).