Fig. 3. Four sources for gut microbial signaling molecules.
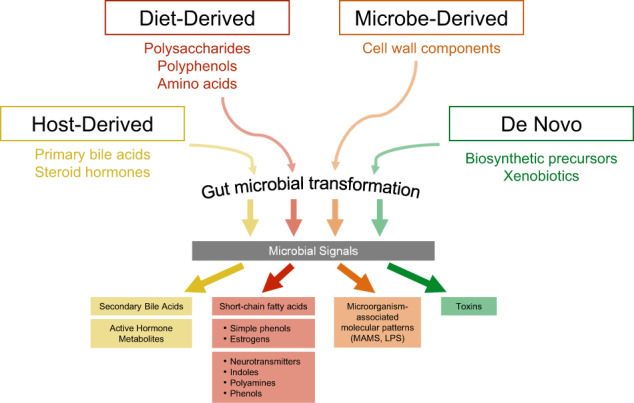
Gut microbial signaling molecules are derived from at least 4 different sources: Diet-derived, microbe-derived, host-derived and newly synthesized molecules. Chemical transformation of these molecules results in a vast number of signaling molecules which can influence not only cells in the gut (immune, nerve, endocrine cells), but following dissemination throughout the body are able to modulate all organs, including the brain. Certain diet-derived microbial metabolites have neuroactive effects on the central and autonomic nervous system, while microbial cell wall components can activate the immune system by interacting with TLRs. Some microbial metabolites (in particular the SCFA butyrate) exert anti-inflammatory effects. Modified with permission from Needham et al., 2020.
