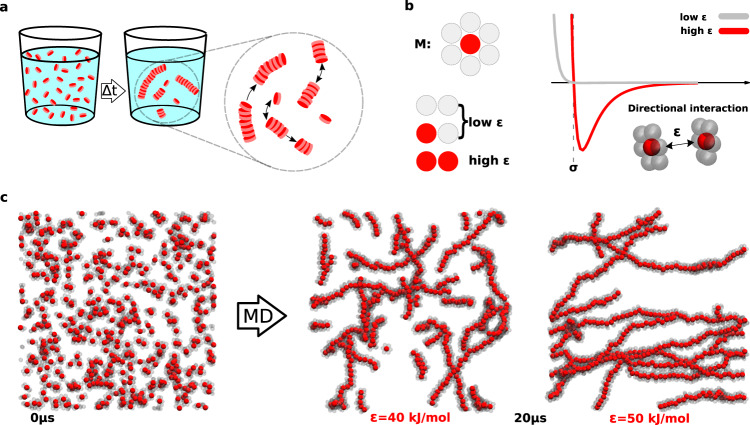
Fig. 1. Minimalistic model of self-assembling monomers M.
a Scheme for the self-assembly of monomeric M units into supramolecular polymers. At the thermodynamic equilibrium, the fibres exhibit a more/less pronounced dynamic behaviour, exchanging units and fragments with each other and with the external environment. b Structure and interaction of the minimalistic model: the M monomers interact directionally via attractive interaction between the central red beads. Weakly interacting beads (in grey) are added to screen the red beads and prevent lateral binding of the monomers (imparting directionality to the M–M interaction). The interactions in the model are defined by Lennard–Jones potentials. c CG-MD simulation snapshots of a model system composed of 500 initially randomly distributed monomers: the two snapshots at tCG = 20 μs refer to cases with the interaction strength between central beads is set at ϵ = 40 kJ mol−1 (centre) or ϵ = 50 kJ mol−1 (right), respectively, (both model systems start from the same initial condition, on the left).