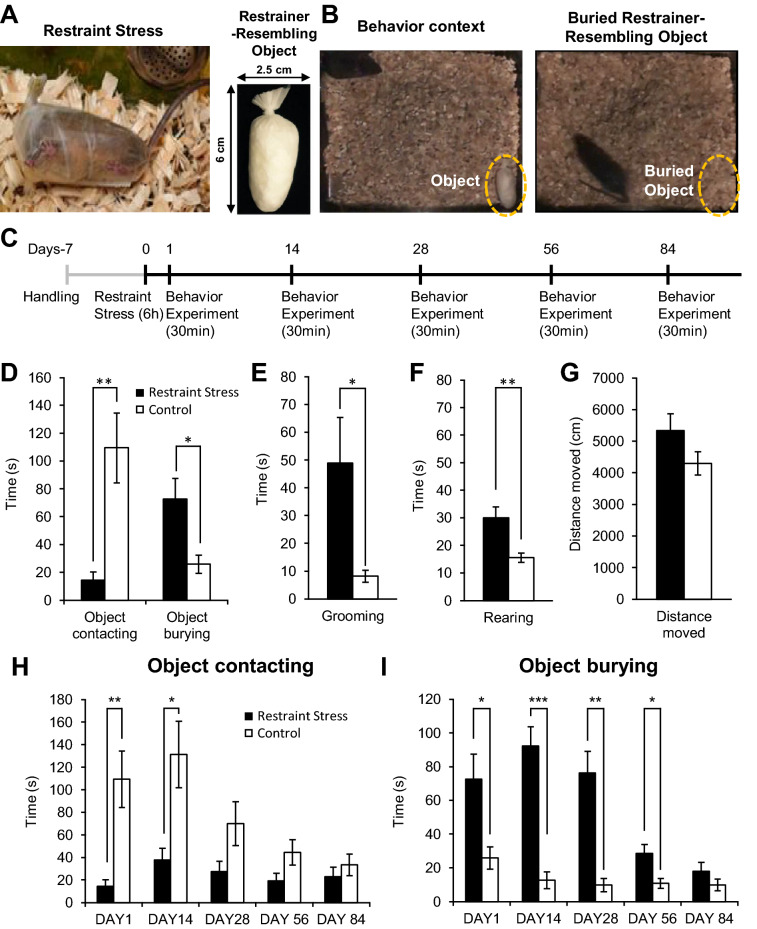
Figure 1.
Fear and anxiety-like behaviors induced by acute restraint stress. (A) Images of a mouse experiencing restraint stress (left) and a restrainer-resembling object (right). (B) Image of an experimental setting (left) and an exemplarily image of a restrainer-resembling object buried by a stressed mouse (right). (C) The timeline of experiments. (D) Contacting and burying of a restrainer-resembling object in stressed and control mice in the first experiment (day 1). Contacting behavior includes biting, carrying, touching, and manipulation of a restrainer-resembling object. (E) Cumulative duration of grooming behavior during in the first experiment (day 1) between groups. (F) Rearing behavior (also known as the attempt of escape behavior) of mice in the first experiment (day 1). (G) Total distance moved of mice during in the first experiment (day 1). (H) Changes in contacting behavior of the restrainer-resembling object over time between stress and control groups. (I) Changes in restrainer-resembling object burying behavior over time between stress and control groups. (D–I) Control (n = 8), Restraint stress (n = 8). All data are presented as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM). Student’s t-test was used to compare means between the stress and the control group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.