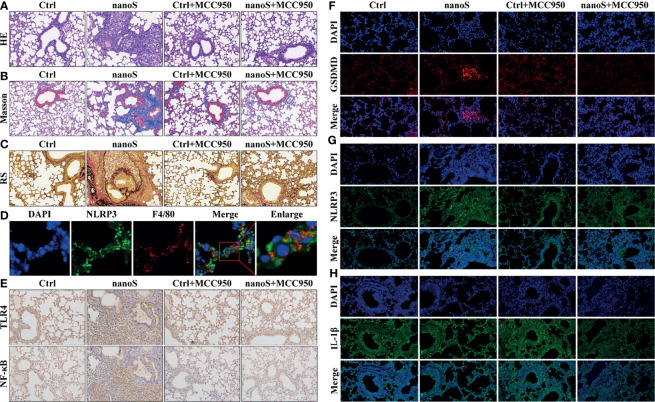
Figure 6.
Silica induces macrophage pyroptosis and triggers pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. (A) Images of hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining showing the pathological changes of the lung tissues (20× magnification). The nuclei are stained in blue by hematoxylin, and the cytoplasm is stained in red by eosin. (B) Images of Masson staining showing the expression of collagen fibers (20× magnification). The collagen fibers are stained in blue, and the cytoplasm is stained in red. (C) Images of Resorcin-Fuchsin staining showing the expression of collagen fibers (20× magnification). The collagen fibers are stained in red; the muscle fibers are stained in purplish red, and other contents are stained in yellow. (D) Images of dual immunofluorescent staining showing the co-expression of NLRP3 and F4/80 within the cells. Blue, nuclei; Red, macrophage; Green, NLRP3. (E) Images of immunohistochemistry showing pulmonary expression of TLR4 and NF-κB (20× magnification). The positive areas are stained in brown. (F–H) Images of immunofluorescent staining showing the expression of GSDMD, NLRP3, and IL-1β (20 × magnification). The nuclei are stained in blue by DAPI, GSDMD is stained in red, NLRP3 and IL-1β are stained in green by specific antibodies.