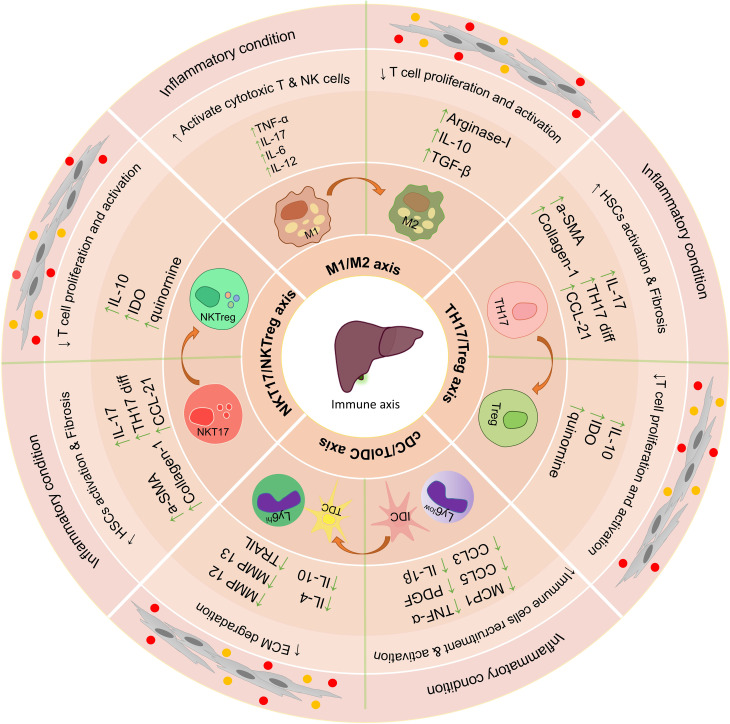
Figure 3.
The effect of using mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles on the important axis of the immune system in the liver. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their extracellular vesicles lead to the suppression of inflammatory responses in the liver’s microenvironment and increase anti-inflammatory responses. Some of the most important axis of the immune system involved in liver disease is TH17/Treg, NKT17/NKTreg, and M1/M2. The use of mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles leads to suppression of function Th17, NKT17, M1, and IDC and increase the differentiation and function of Treg, NKTreg, M2, and Tol DCs; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; KCs, Kupffer cells; LSECs, hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells; HEPs, Hepatocytes; Tol DCs, Tolerogenic dendritic cells; cDC, Classic dendritic cells; ECM, extracellular matrix; MSCs, Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells;, M1 Macrophage type 1; M2, Macrophage type 2; MMPs, Matrix metalloproteinase; EVs, Extracellular vesicles.