Figure 3.
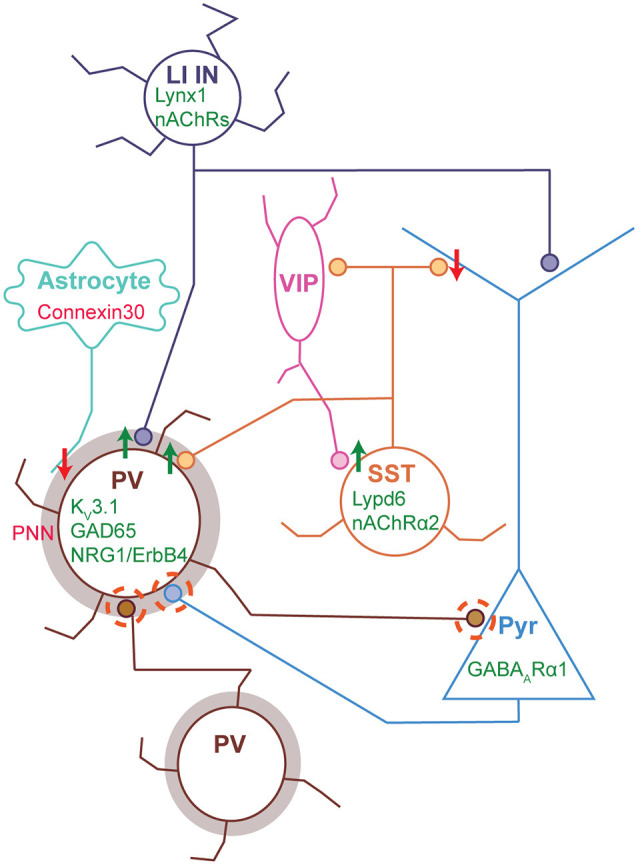
Molecular and synaptic loci of plasticity during sensory critical periods. Cortical circuit schematic with major synaptic connections and molecular factors regulating critical period plasticity. The circuit depicted shows the circuit motifs and cellular components regulating CP plasticity: basket PV INs (Brown) inhibit one another and exert strong inhibitory control of Pyr (light blue) through perisomatic inhibition; layer I INs (dark blue) inhibit the apical dendrites of Pyr and can also target PV cells, resulting in simultaneous Pyr somatic disinhibition and dendritic inhibition; Martinoti SST INs (yellow) across layers target Pyr apical dendrites and also receive input from VIP INs (pink), such that VIP activation results in Pyr disinhibition; while a subset layer IV SST INs target PV INs preferentially, resulting in disinhibition; and astrocytes regulate the extracellular matrix and PNN formation onto PV INs. PV IN maturation determines both the onset and closure of cortical critical periods. Maturation of PV intrinsic properties, synaptic inputs (both excitatory and inhibitory, dashed circles), and inhibitory synaptic output onto Pyr (dashed circle) are all crucial for CP plasticity. Expression of KV3.1, GAD65 and NRG1/ErbB4 in PV INs promote (green) normal CP plasticity (Hensch et al., 1998; Matsuda et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2021), while PNN (brown shadow) maturation in PV INs prevent and close CP plasticity (Pizzorusso et al., 2002; Nowicka et al., 2009; Sigal et al., 2019). In addition, GABAAα1 receptor expression in Pyr (in putative PV synapses) is necessary for CP plasticity (Fagiolini et al., 2004). Both SST and LI INs can induce CP plasticity indirectly by means of PV IN inhibition, such that the expression of molecular factors promoting SST (Lypd6 and nAChRα2) or LI IN (Lynx1 and nAChRs) activity enhance plasticity (Takesian et al., 2018; Sadahiro et al., 2020). On the other hand, VIP IN-mediated Pyr disinhibition, via SST inhibition, also promotes cortical plasticity (Fu et al., 2015). In contrast, connexin 30 expression in astrocytes restricts CP plasticity via PNN maturation in PV INs (Ribot et al., 2021). Green font/arrows represent molecules or synapses promoting CP plasticity, while red font/arrows represent those preventing plasticity. Abbreviations: PV, Parvalbumin; Pyr, Pyramidal cell; SST, Somatostatin; LI INs, Layer I interneurons; VIP, Vasoactive intestinal peptide; PNN, Perineuronal net; nAChRs, Nicotinic Acetylcholine receptors; NRG1, Neuregulin 1; KV3.1, Potassium channel 3.1; GAD65, Glutamic acid decarboxylase 65-kilodalton.
