Figure 2.
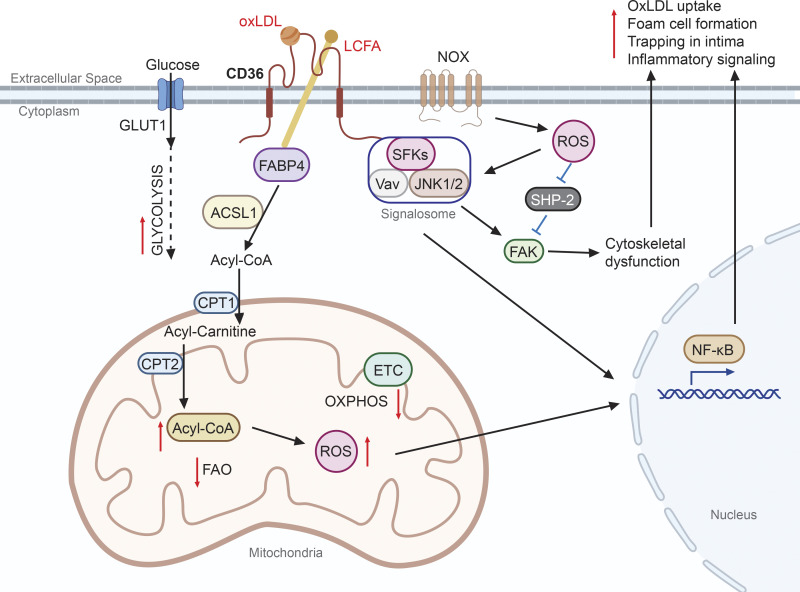
CD36 mediates macrophage activation. oxLDL binds to extracellular domains of CD36, which promotes both signaling cascades and lipid uptake. The CD36 cytosolic tail recruits a signalosome complex including SFKs, JNK1/2, and Vav, which is also enhanced by NOX-derived ROS. Both signalosome and ROS (by inhibition of SHP-2) activate focal adhesion kinase (FAK), which leads to dysregulated cytoskeletal dynamics. Meanwhile, extracellular LCFA is transported into the cell via CD36 and then into mitochondria matrix through a series of transport machinery interactions including FABP4, ACSL1, CPT1, and CPT2. LCFA influx to mitochondria facilitates a metabolic switch from OXPHOS to glycolysis, accompanied by a reduction in FAO and increase in ROS production. The signaling cascades and metabolic switch in combination results in NF-κB pathway activation and proatherogenic responses including pro-inflammatory activation, oxLDL uptake, foam cell formation, and trapping of macrophages in the neointima.