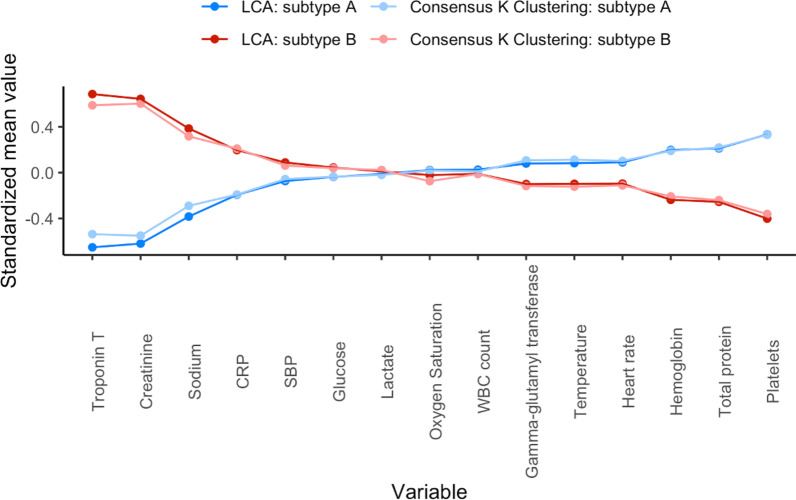
Fig. 2.
Comparison of class-defining variables using latent class analysis and consensus k means clustering. Description: continuous variables were plotted after natural log transformation. Every normalized variable was standardized such that all means are scaled to 0 and SDs to 1. Group means of standardized values are shown by subtype classes (A and B). A value of + 1 for the standardized variable (y-axis) indicates that the mean value for a given subtype was one SD higher than the mean value in the whole sepsis-survivors cohort (N = 467). Subtype classes sizes (n): Latent class analysis: subtype A N = 244, subtype B N = 223; consensus k means clustering: subtype A N = 255, subtype B N = 212 (concordance rate (accuracy) = 81%). The mean (± SD) of percent missingness of the 15 class-defining variables was 12% (± 6). No significant difference in missing information for class-defining variables was found between subtypes A and B at ICU discharge (Chi square test). Abbreviations: SD standard deviations, BUN blood urea nitrogen, CRP C-reactive protein, SBP systolic blood pressure, WBC white blood cell, ICU intensive care unit