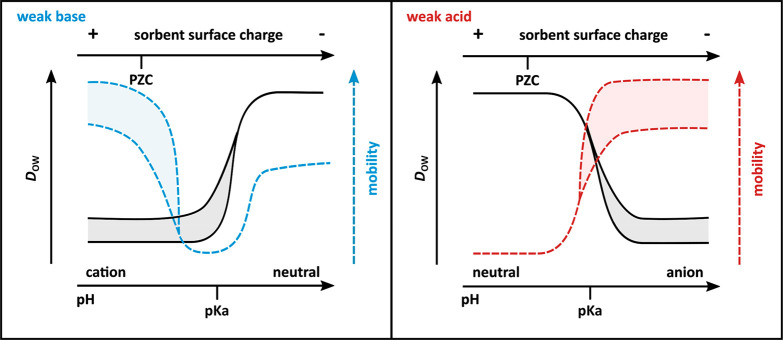
Figure 1.
Mobility of IOC in soils and sediments depends not only on hydrophobicity, but is additionally affected by the surface charge of soil constituents, pore water chemistry, and IOC speciation. PZC = sorbent point of zero charge; above this pH overall surface charge is negative, Dow = water-chemistry dependent octanol–water partitioning coefficient, pKa = IOC dissociation constant. Black solid lines and colored dashed lines represent hydrophobicity and mobility, respectively. The colored ranges represent the influence of counterion concentration.