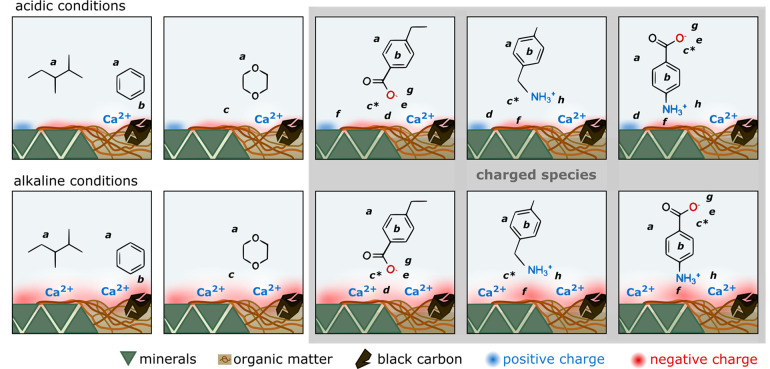
Figure 3.
Key drivers and interactions for sorption of different groups of organic compounds under acidic conditions (top row) and alkaline conditions (bottom row). Compound groups with representative examples from left to right: neutral nonpolar compounds, neutral polar compounds, anionic compounds, cationic compounds, and zwitterionic compounds. Panels with charged species are highlighted in gray. Possible drivers and interactions: a = hydrophobic effect, b = π–π electron donor–acceptor interaction, c = H-bond, c* = charge assisted H-bond, d = electrostatic repulsion, e = cation bridging, f = electrostatic attraction, g = anion – π bond, h = cation – π bond.