Fig. 3. NRP1 is associated with increased suppressive function.
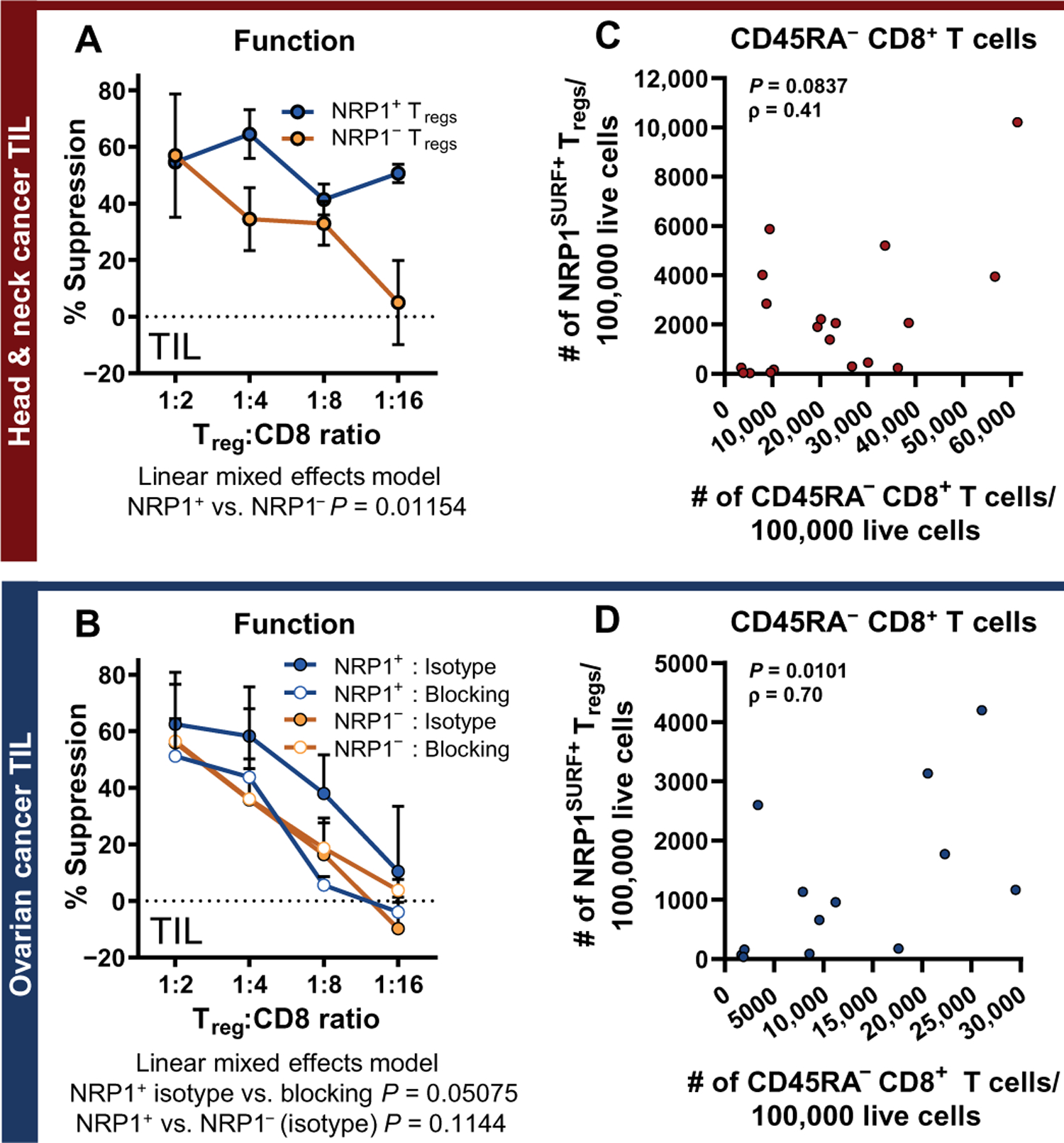
(A and B) Microsuppression assay comparing NRP1+ and NRP1− Tregs isolated from the same tumors are shown. Data are presented as means + SEM. Data are pooled from multiple experiments [three experiments for (A); four experiments for the NRP1SURF− group in (B) and two experiments for the NRP1SURF+ group in (B)]. Significance was analyzed by comparing the linear mixed effects model for the dataset to a null model via likelihood ratio test. A targeted NRP1 antagonist (10 μg/ml) was compared to the isotype control and reduced the suppressive function of OvCa intratumoral NRP1+ Tregs (P = 0.05075). (C and D) Nonparametric (Spearman’s) correlation is shown for the intratumoral count of NRP1SURF+ Tregs with the intratumoral count of CD45RA− CD8+ T cells (both normalized to 100,000 live cells) in samples of HNSCC (n = 19) and OvCa (n = 13), respectively.
