FIG 1.
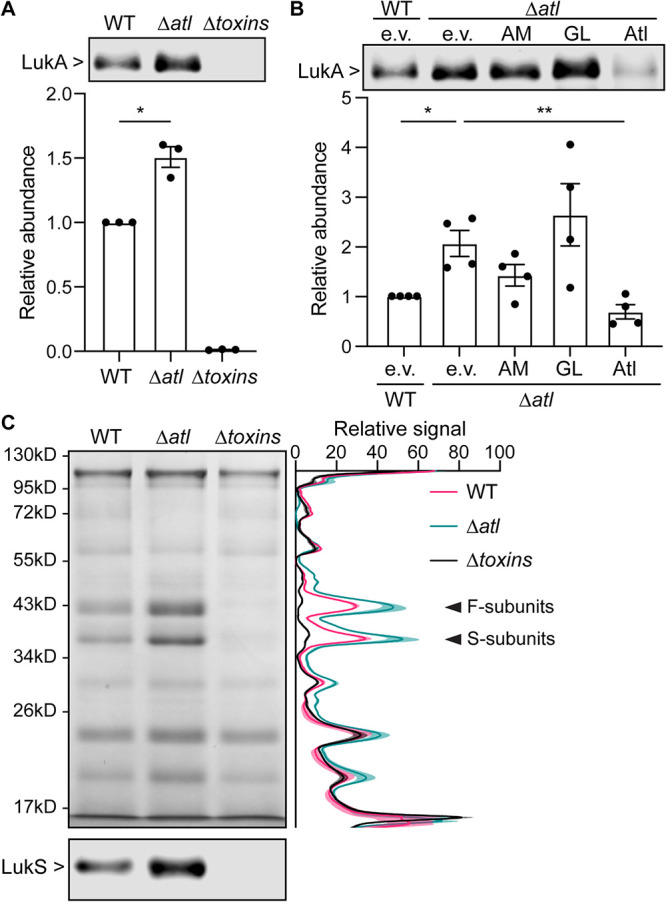
Atl influences the secretion of leukocidins. (A) Immunoblot of LukA in the culture supernatant of WT, the atl mutant, and a mutant strain depleted of all pore-forming toxins (Δtoxins). A representative immunoblot (top) and the mean ± SEM of the LukA signal from 3 independent experiments are shown (bottom). *, P ≤ 0.05 comparing WT and the atl mutant by a paired t test. (B) Immunoblot of LukA in the culture supernatant of WT containing empty vector (e.v.) and the atl mutant containing the indicated Atl domains or full-length Atl. A representative immunoblot (top) and the mean ± SEM of LukA signal from 4 independent experiments (bottom) are shown. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01 by repeated-measures (RM) one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple-comparison tests. (C) Exoprotein profile as detected in an InstantBlue-stained SDS-PAGE (top) and immunoblot of leukocidin S subunits (bottom) of indicated strains. Signals of the InstantBlue-stained SDS-PAGE from 3 independent experiments were quantified and plotted on the right. Shaded area indicates SEM. The arrows point to the bands at the size of leukocidins. The immunoblot is a representative image of 3 independent experiments.
