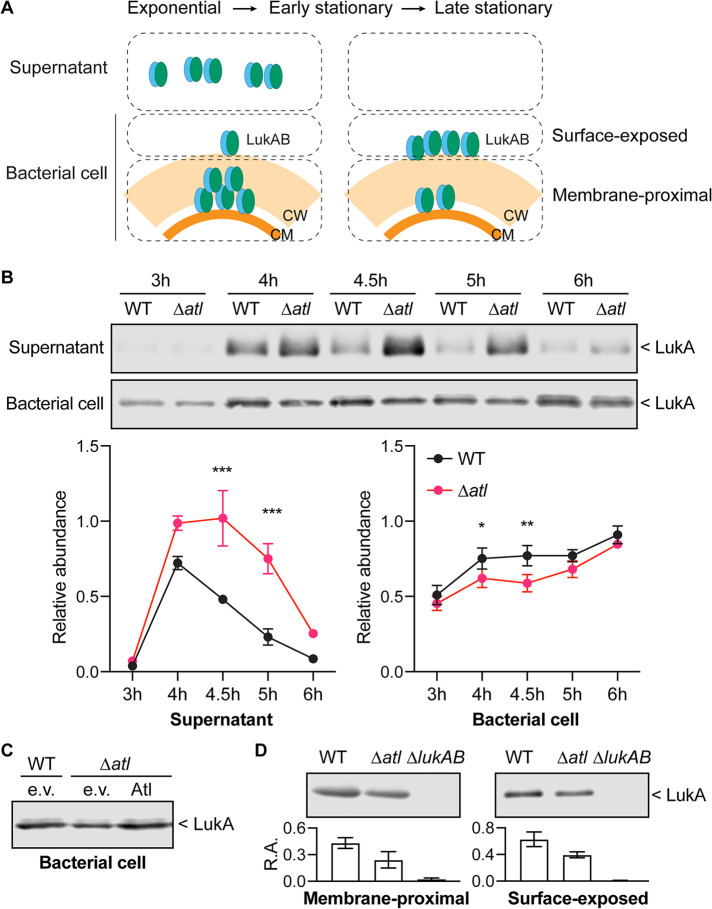
FIG 4.
Sorting of LukAB in the atl mutant. (A) Diagram of LukAB localization with different compartments of the cell envelope. LukAB is secreted into the culture supernatant at the exponential and early-stationary phases but is absent in the supernatant at the late-stationary phase. LukAB can be found associated with the bacterial cells in all growth phases. The bacterial cell can be further separated into the membrane-proximal and surface-exposed compartments. Most LukAB is found in the membrane-proximal compartment at the exponential phase but in the surface-exposed compartment at the late-stationary phase. CM, cell membrane. CW, cell wall. (B) Representative immunoblots of LukA in the cultures from different growth times (top) and the quantification of the LukA signal in the culture supernatant or associated with the bacterial cell from the immunoblot results (bottom). The signal was normalized to 50 ng purified recombinant LukAB on each membrane. Data show mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001 by two-way ANOVA with Sidak multiple-comparison test. (C) Immunoblot of LukA associated with the bacterial cell in WT containing empty vector (e.v.), the atl mutant containing empty vector (e.v.), or plasmid-expressed full-length Atl. Figure shows a representative immunoblot from 3 independent experiments. (D) Representative immunoblots (top) and quantifications of the LukA signal (bottom) in the membrane-proximal or surface-exposed compartments associated with the bacterial cell. Relative abundance (R.A.) of LukA signal was normalized to 50 ng purified recombinant LukAB on each membrane. Data show mean ± SEM from 3 independent experiments. P values between WT and Δatl determined by two-tailed paired t tests as follows: membrane proximal, 0.04; surface exposed, 0.12.