FIG 2.
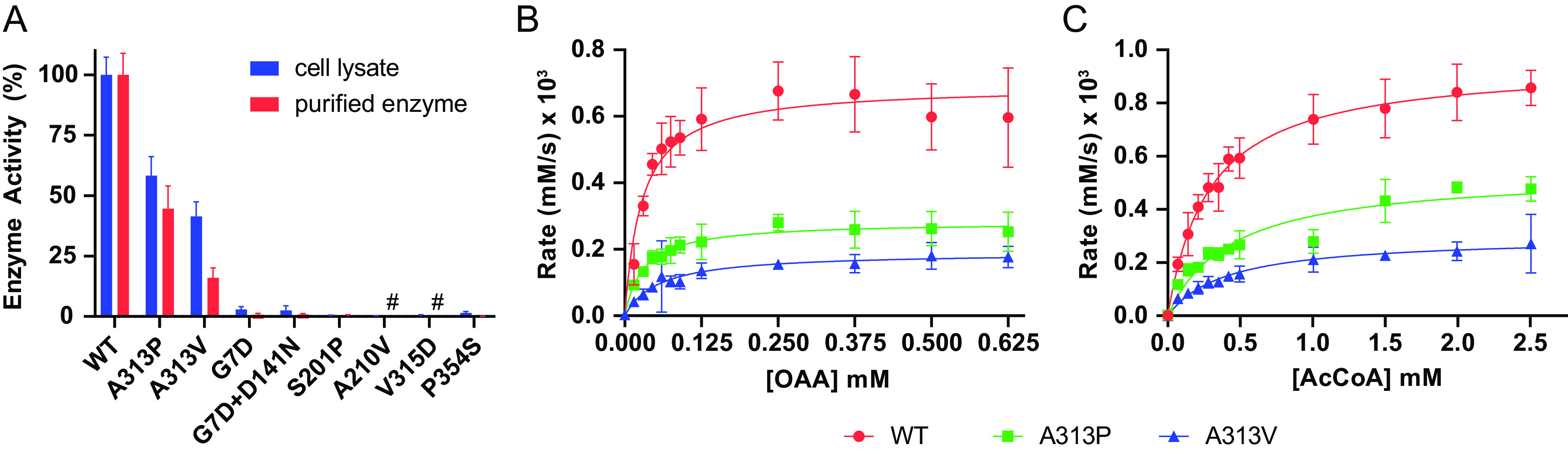
citZ mutations cause a loss of citrate synthase activity. (A) Percent citrate synthase activity. CS rates were measured using the lysate of each clinical isolate harboring a citZ mutation (blue) and the corresponding purified recombinant CS protein containing the same mutation (red). Rate values are normalized to respective wild-type (100%) and buffer-only controls (0%). Data points and error bars represent the mean and 95% confidence intervals of at least three independent replicates, respectively. #, denotes mutants with no purified enzyme data due to poor expression. (B and C) Plots of CS rate versus substrate concentration for wild-type (WT) and A313 mutants (A313P and A313V). (B) Variable oxaloacetic acid (OAA) with acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) fixed at 0.3 mM. (C) Variable AcCoA with OAA fixed at 0.5 mM. Data points and error bars represent the mean and 95% confidence intervals of independent replicates (n = 3), respectively. Plotted curves indicate best fits from nonlinear regression using the Michaelis-Menten equation. See Table S3 for values of fitted parameters (kcat and Km).
