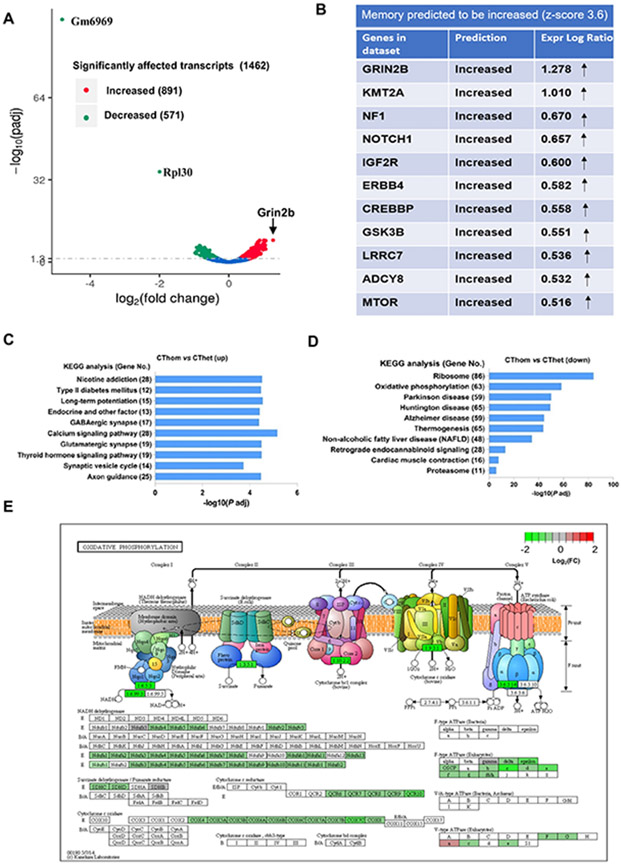
Figure 3. nSMase2-sensitive transcripts are related to oxidative phosphorylation, ribosome biogenesis, synaptic transmission, plasticity, and memory.
(A) Volcano plot shows differentially abundant transcripts in homozygous (fro/fro) vs. heterozygous (+/fro) mouse cortex. Red labels denote increased and green decreased transcripts in fro/fro cortex. The two transcripts decreased most are cytochrome c oxidase subunit VIIa polypeptide 2-like pseudogene (Gm6969) (and ribosomal protein L30 (RPL30). The transcript most increased is Grin2b (NMDA receptor subunit 2B, arrow). (B) IPA analysis shows that Grin2b is one of a set transcripts encoding proteins important for memory that are increased in fro/fro mice. (C, D) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of over-represented functional relationships among transcripts increased in fro/fro (CThom) cortex as compared to +/fro (CThet) cortex, showing the top 10 most significant biological pathways. (E) KEGG pathway analysis of oxidative phorphorylation shows the protein assembly in oxidative phosphorylation depicting five mitochondrial complexes containing proteins encoded by transcripts decreased in fro/fro mice. The color legend represents fro/fro vs. +/fro log2FC with red denoting upregulation, green denoting downregulation, and grey indicating log2FC is zero.