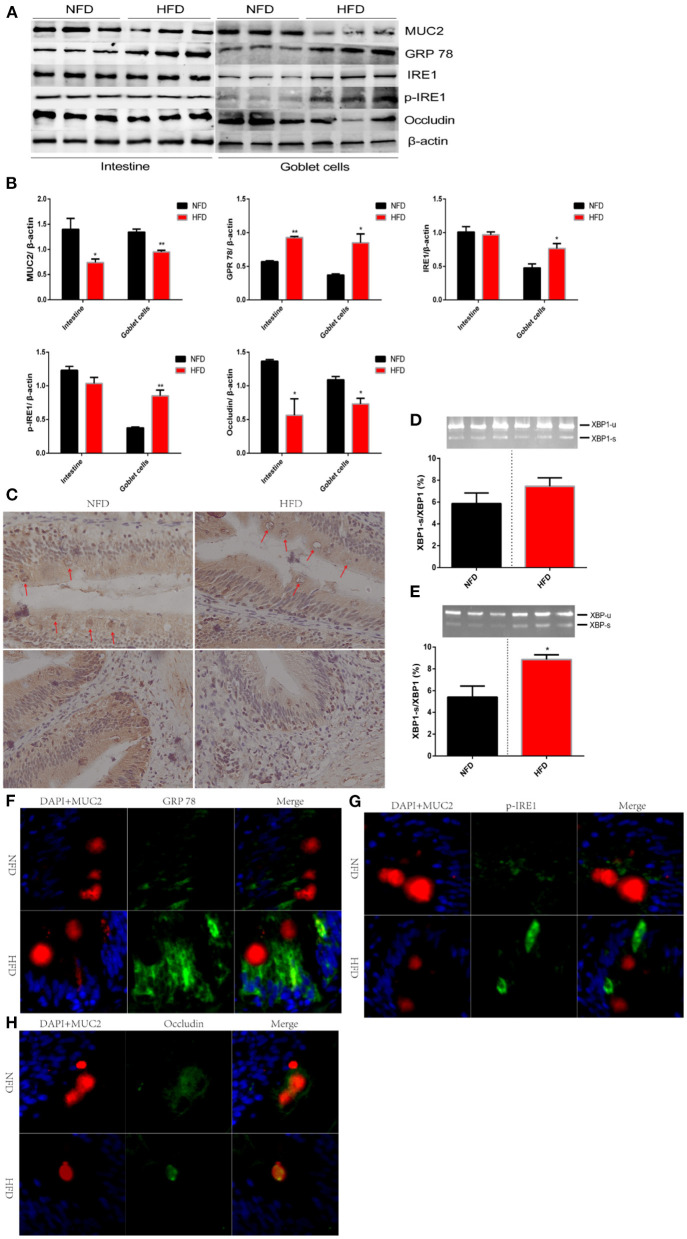
Figure 4.
High-fat diets increase intestinal permeability via disturbing the secretion of MUC2 in goblet cell. Fish were fed a normal-fat diet (5% fat, NFD) or high-fat diet (10% fat, HFD) for 12 weeks. (A) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of MUC2, GPR 78, IRE1, p-IRE1 and occludin in intestinal tissue or isolated goblet cells. (B) Quantitative western blot analysis of MUC2, GPR 78, IRE1, p-IRE1 and occludin in intestinal tissue or isolated goblet cells. (C) Immunohistochemical analysis for the distribution of MUC2 in the intestinal tissue. Goblet cells are marked with red arrows. (D,E) The ratio of spliced to unspliced XBP1 mRNA in ntestinal tissue (D) or isolated goblet cells (E). (F–H) Immunofluorescence analysis for the relocalization of GPR 78, p-IRE1 and occludin. The nucleus is stained by DAPA (blue), goblet cells is stained by MUC2 (red) and GPR 78 (F), p-IRE1 (G) and occludin (H) is stained by corresponding antibody (green). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. N = 4. Two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test was used. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.