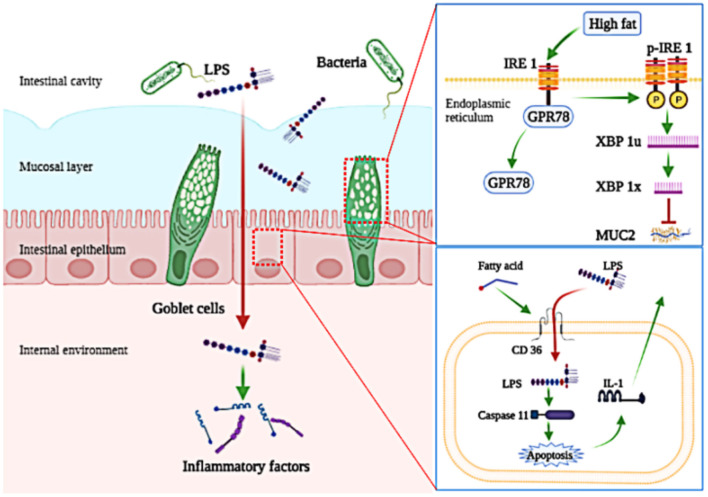
Figure 7.
A schematic diagram shows key molecular pathways involved in the penetration of LPS induced by high-fat diet. Consumption of high-fat diets increases the penetration of LPS, which induces low-grade chronic inflammation; Consumption of high-fat diets inhibit the secretion of MUC2 by activating the IRE1/XPB-1 signaling pathway in goblet cells; Fatty acids assist in the cellular internalization of LPS and then activate its intracellular signaling pathway depending on CD36 in intestinal epithelial cells.