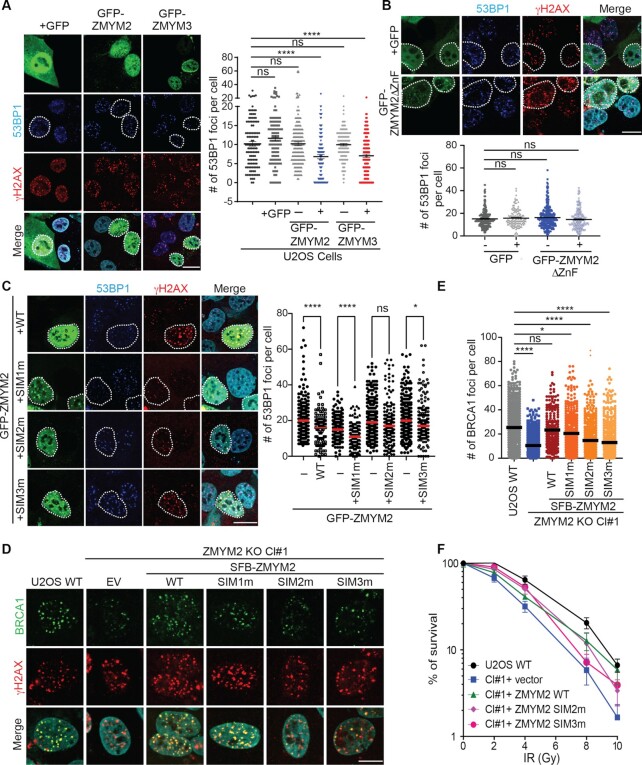
Figure 8.
ZMYM2 antagonizes 53BP1 at damage sites via SUMO binding. (A) ZMYM2 and ZMYM3 overexpression reduces 53BP1 IRIF. U2OS cells expressing GFP, GFP-ZMYM2, or GFP-ZMYM3 were analyzed for 53BP1 and γH2AX foci formation following IR treatment (10 Gy, 3h) by IF. Right panel: quantification of total number of 53BP1 foci per cell after IR treatment. Data represented as mean ± S.E.M. from >90 cells, n = 3, scale bar = 20 μm, (ns; not significant, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA test). (B) The ZnF domains of ZMYM2 are required to antagonize 53BP1 at IR-induced breaks. Analysis was performed as in a with GFP or GFP-ZMYM2ΔZnF expressing U2OS cells. lower panel: quantification of total number of 53BP1 foci per cell after IR treatment. Data represented as mean ± S.E.M. from >120 cells, n = 3, Scale bar = 20 μm (ns; not significant, one-way ANOVA test). (C) ZMYM2 SIM2 and SIM3, but not SIM1, are required to inhibit 53BP1 IRIF. Analysis was performed as in (A). Data represented as mean ± S.E.M. from >100 cells, n = 3 (ns; not significant, *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA test). (D, E) ZMYM2 SIM2 and SIM3 mutants, unlike WT ZMYM2, are unable to complement deficient break association of BRCA1 that is observed in ZMYM2 KO cells. Experiments were performed as in Figure 4B. Quantification of number of BRCA1 foci per cell in each sample is provided in (E) (ns; not significance, *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA test). (F) IR sensitivity of ZMYM2 KO cells complemented with WT ZMYM2 and derivatives. Experiments were performed as in Figure 2C with the indicated ZMYM2 WT and mutant clones.