Figure 9.
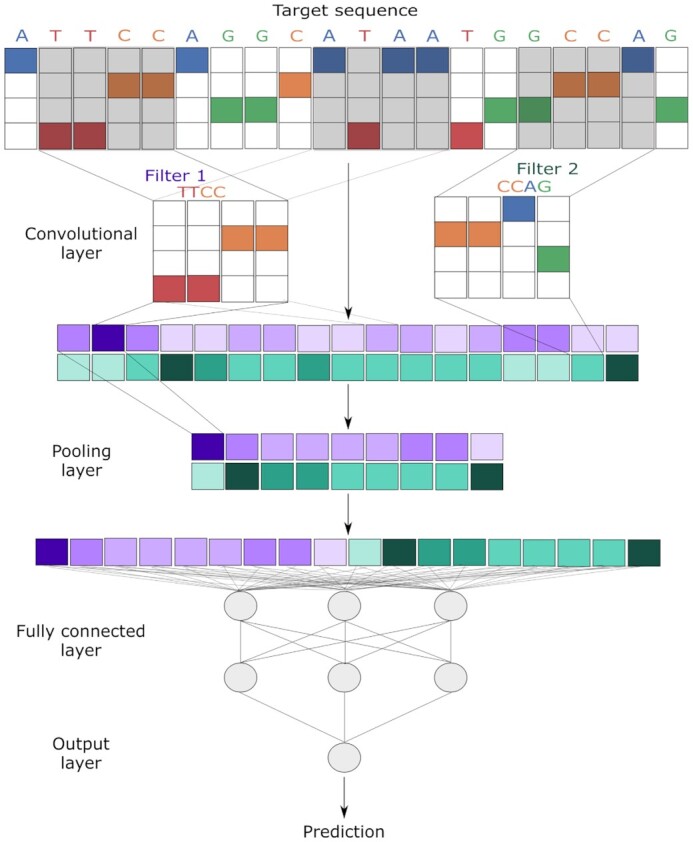
An example of a CNN being used to extract features from DNA sequences. First, the sequence is encoded by ‘one-hot’ vectors with a 1 at the position corresponding to the nucleotide type (A, C, G or T), and zero otherwise. The convolution and pooling operations are then applied to the input vectors to produce the output of each layer as a feature map. In this example, the convolutional layer includes two (4 × 4) filters that detect sequence motifs, while the pooling layer aggregates their output using the maximum pattern match. Finally, the output of the fully connected layers is fed to a regression layer that assigns a score to the given sequence.
