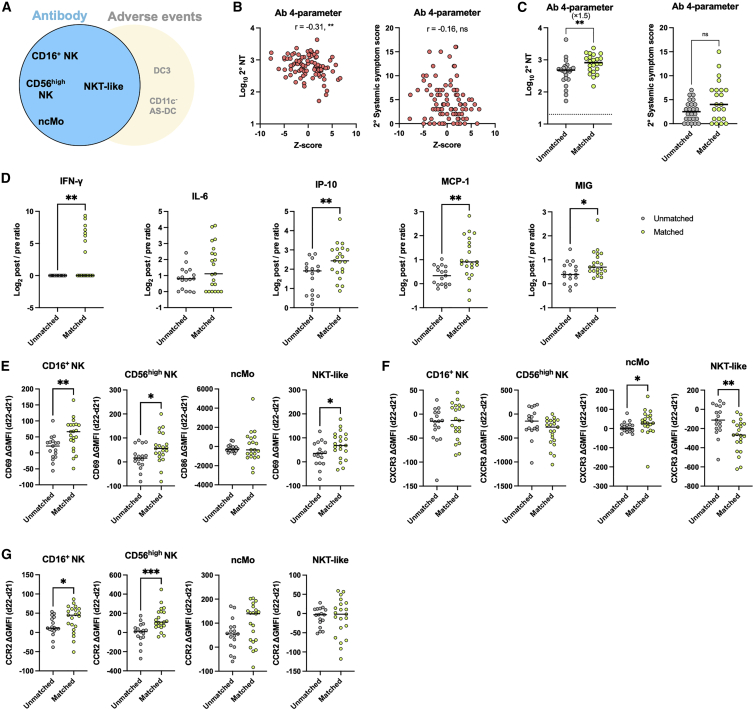
Figure 6.
The combination of NK, NKT, and monocyte subset dynamics classify a subgroup of vaccinees with high neutralizing-antibody responses
(A) Scheme of the 4-parameter model related to antibody responses.
(B) Z score calculated based on four parameters (i.e., the post/pre ratios of NKT-like, CD16+ NK, CD56high NK, and non-cMOs [ncMos]). Correlation of Z score and NT titers at days 47–51 and systemic-symptom-severity scores. n = 92.
(C) Participants were stratified into matched and unmatched groups for the 4-parameter model related to antibody responses. NT titers and systemic-symptom-severity scores compared between matched and unmatched groups. Matched group, n = 22; unmatched group, n = 24.
(D) Cytokine dynamics (d22–d21 post/pre ratios) are compared between Ab-related matched and unmatched groups. Matched group, n = 21 (d21), n = 22 (d22); unmatched group, n = 17 (d21), n = 18 (d22) (Ab 4-parameter).
(E–G) Differences in expression levels of CD69 or CD86 (E), CXCR3 (F), and CCR2 (G) between d22 and d21 were compared between Ab-related matched and unmatched groups. Matched group, n = 21 (d21), n = 22 (d22); unmatched group, n = 17 (d21), n = 18 (d22) (Ab 4-parameter). GMFI, geometric mean fluorescence intensity. Bars represent the median, and each dot represents data for an individual participant in (C)–(G).
Statistical significance is indicated as follows: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney test in (C)–(G) (matched versus unmatched groups), Spearman’s rank-order coefficient test in (B). Spearman’s r values are indicated above the plots in (B).
See also Figure S7.