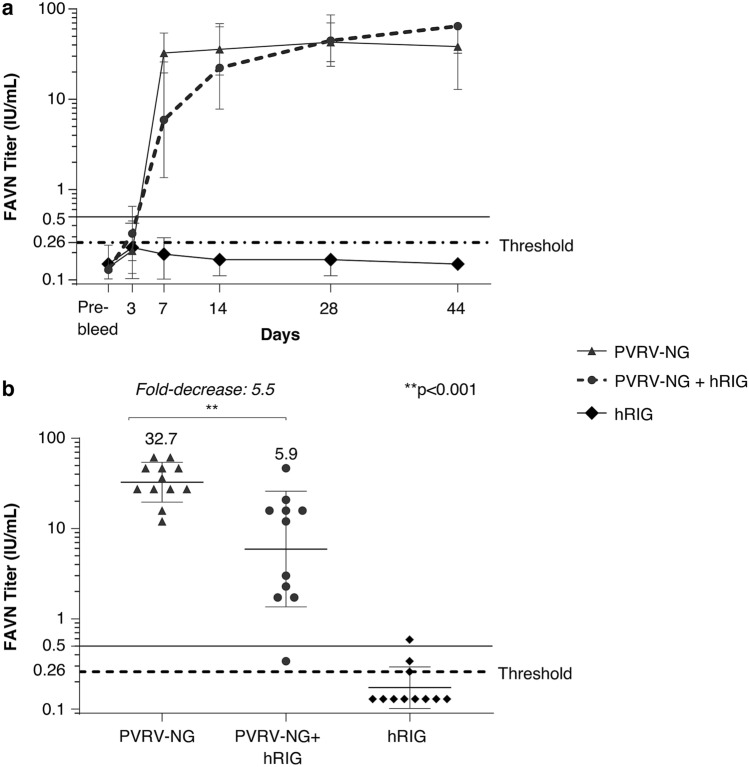
Figure 2.
Immunogenicity of PVRV-NG vaccine in presence of human rabies immunoglobulin (hRIG) administered by intramuscular (IM) injection according to post-exposure prophylaxis regimen. In the preliminary experiment to set up the animal model, adult female hamsters (n = 12 per group) were vaccinated on Days 0, 3, 7, 14, and 28 by IM injection with 1:5 Human Dose of PVRV-NG in one group, and co-injected with hRIG (20 IU/kg) on Day 0 in another group. (a) Serum rabies virus neutralizing antibody (RVNA) levels were monitored by performing a fluorescent antibody virus neutralization test (FAVN) on blood samples collected on Days -7 (7 days prior to Day 0; pre-bleed), 3, 7, 14, 28, and 44. The lower level of detection in FAVN was of 0.26 IU/mL as shown by the dotted line. The continuous black line indicating 0.5 IU/mL is the WHO specified standard serum RVNA titer considered as an adequate immune response to rabies vaccination in humans. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. (b) Serum RVNA titers measured 7 days after the first immunization.