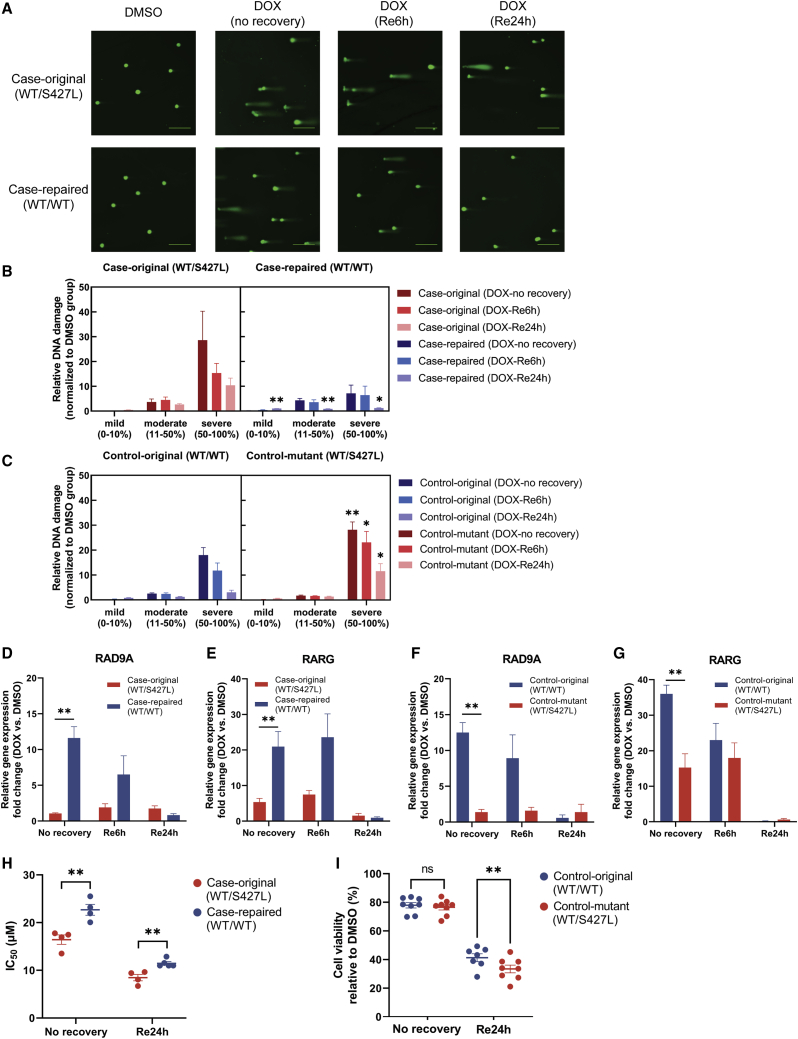
Figure 4.
Impact of RARG-S427L on doxorubicin-induced DNA damage and repair
(A) Comet assay results visualized under fluorescence microscope (scale bars represent 200 μm).
(B and C) Relative DNA damage fold change in RARG-WT/WT and RARG-WT/S427L assay (n = 3; 100–150 cells were quantified per sample in each independent experiment).
(D–G) Gene expression of DNA repair gene (D and F) RAD9A and (E and G) RARG with 6 and 24 h of recovery after doxorubicin treatment in DIC-case cell lines measured by qPCR (n = 3).
(H and I) IC50 and cell viability percentages after 24 h of doxorubicin treatment with no recovery time or with 24 h of recovery (n = 4–8). All experiments are biological, independent replicates and are shown as mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; t test.