Figure 6.
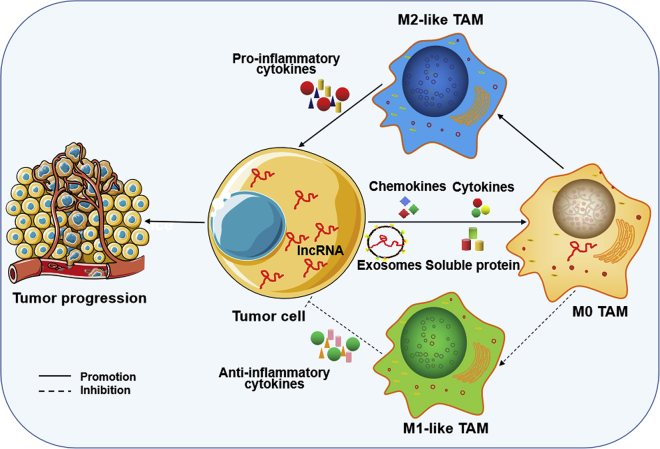
Promoting function of tumor-derived lncRNAs by mediating the crosstalk between macrophages and HCC cells
On the one hand, tumor-derived lncRNA acts as an oncogene in the biological function of the cells from which it originated, and on the other hand, it induces the M2-like polarization of TAMs while inhibiting its M1-like polarization cells through cytokines, chemokines, exosomes, or soluble proteins, thereby prompting macrophages to secrete a large amount of anti-inflammatory cytokines, further enhancing tumor progression.