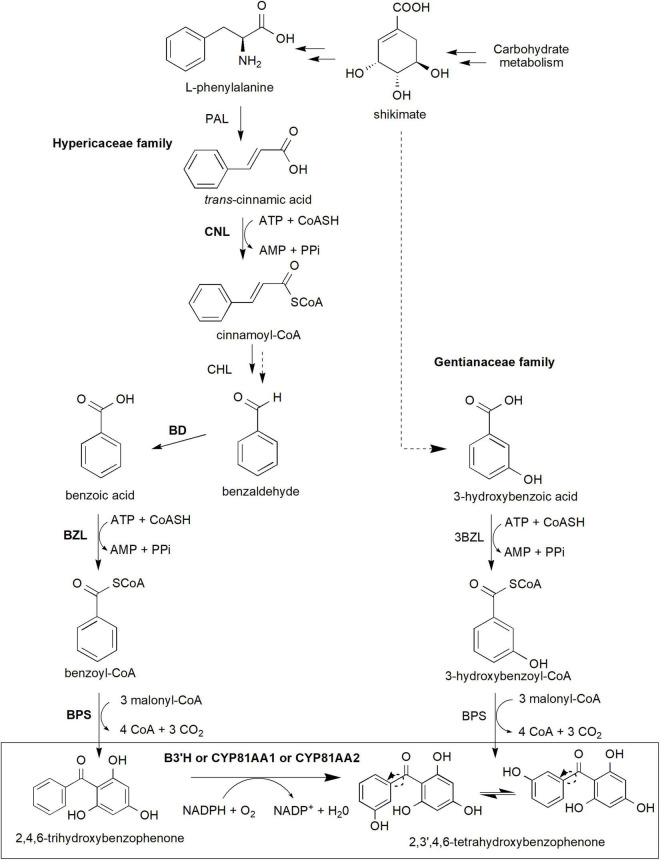
FIGURE 2.
The core xanthone biosynthesis pathway in plants. The shikimate pathway supplies shikimate and L-phenylalanine precursors (detailed pathway is provided in Supplementary Figure 1) to produce benzophenone intermediates, in particular 2,3′,4,6-tetrahydroxybenzophenone isomers used for downstream xanthone biosynthesis. In Gentianaceae family, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid is formed from shikimate and subsequently to 3-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA and later 2,4,5′6-tetrahydroxybenzophenone. Meanwhile, Hypericaceae family utilizes L-phenylalananine-dependent pathway through several more reactions to produce 2,4,6-trihydroxybenzophenone and later the 2,3′,4,6-tetrahydroxybenzophenone. This latter reaction requires B3′H activity of which can be catalyzed by both CYP81AA1 or CYP81AA2 enzymes in Hypericum. Multiple arrows indicate multiple steps between intermediates while dotted arrows indicate hypothesized/proposed pathways. Protein activities that have been detected at molecular level are shown in bold while normal font type indicates protein activities detected at biochemical level (refer to Table 1). The two arrows (one unbroken line and one dotted) for Cinnamoyl-CoA hydratase/lyase (CHL) indicate that the enzymatic reaction has been characterized at the biochemical level from a crude protein extract, but whether this involves one or two enzymatic steps is yet to be validated at the molecular level. 3BZL, 3-hydroxybenzoate-CoA ligase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; BD, benzaldehyde dehydrogenase; BZL, benzoate-CoA ligase; B3′H, benzophenone 3′-hydroxylase; BPS, benzophenone synthase; CHL, cinnamoyl-CoA hydratase/lyase; CNL, cinnamate-CoA ligase; CoASH, coenzyme A; NADPH, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; PPi, inorganic pyrophosphate.