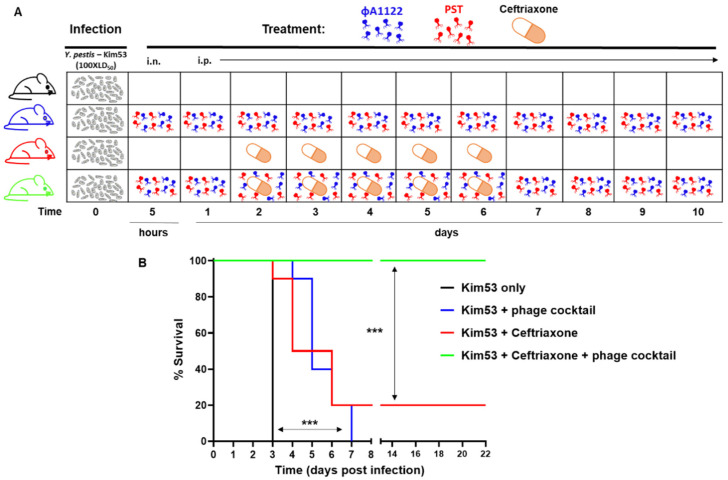
Figure 7.
Effective rescue of infected mice by the phage–antibiotic combination treatment. Schematic presentation of the treatment regimens (A) and survival curves (B) Female C57BL/6J mice were IN infected with 100 × LD50 Y. pestis Kim53. Mouse groups included control nontreated (n = 4), phage-treated (n = 10), ceftriaxone-treated (n = 10) and phage–ceftriaxone combination-treated mice (n = 9). Phage treatment was performed using a phage cocktail composed of фA1122 and PST (1 × 109 each phage/dose; 35 µL for intranasal administration or 0.5 mL for IP injection). Treatment included IN administration at 5 hpi followed by IP injections at days 1–10, with 24 h intervals. Ceftriaxone was subcutaneously injected every 12 h on days 2–6 post bacterial infection. Mice were monitored for 22 days. Statistically significant differences are denoted by asterisks (*** p < 0.001; log rank (Mantel–Cox) test).