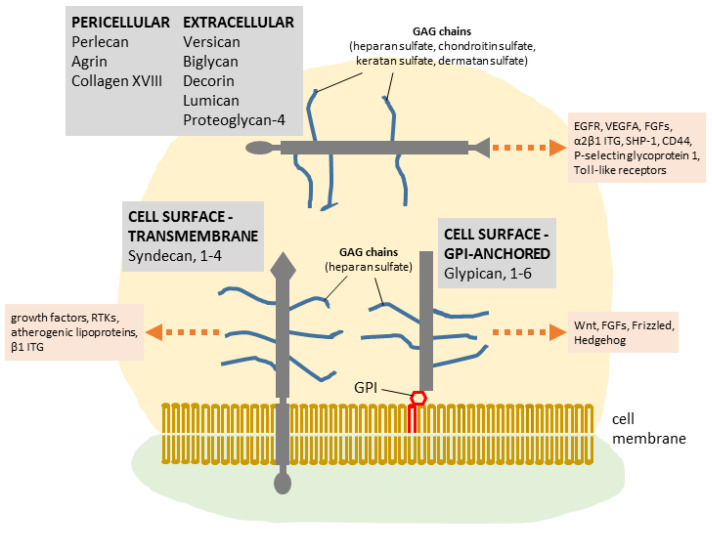
Figure 1.
Proteoglycans generally localize in the cell membrane, pericellular, or extracellular space. Large complexes can form between extracellular proteoglycans and hyaluronan, which can coordinate several units of proteoglycans to form a highly hydrated gel-like matrix (not shown). Multiple interactions occurring between proteoglycans and extracellular ligands, or cell membrane receptors (shown as orange arrows) may modulate their downstream signaling effects. RTKs, receptor tyrosine kinases; ITG, integrins; GPI, glycosylphosphatidylinositol.