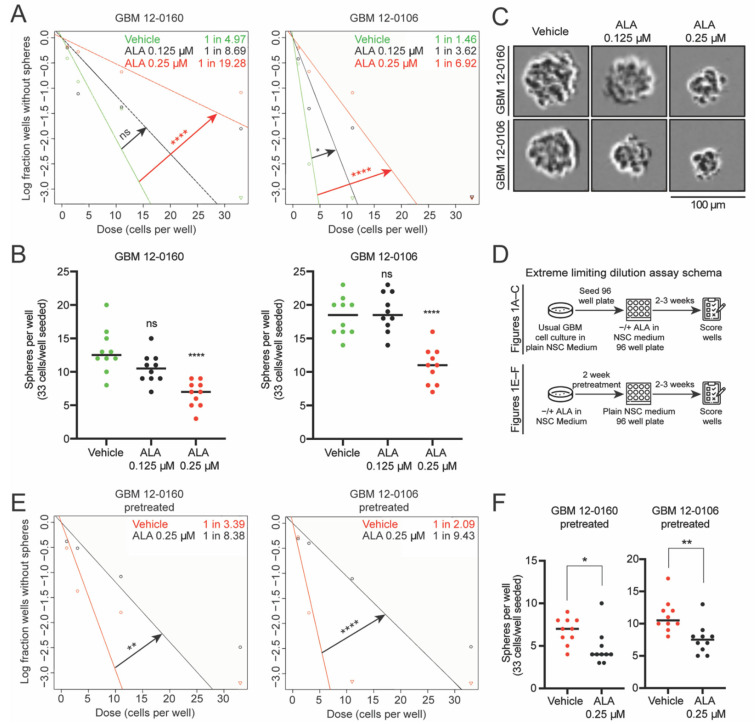
Figure 1.
Inhibition of de novo purine synthesis using L-Alanosine (ALA) decreases stem cell frequency and sphere-forming capacity of MTAP-deficient glioblastoma (GBM) cells. (A) Extreme limiting dilution assays (ELDAs) show ALA treatment decreases stem cell frequency in two MTAP-deficient patient-derived GBM cell lines. Stem cell frequency (1 in n) for each condition shown on plot. 33, 11, 3, 1 cells seeded per well, n = 12 replicates per condition. (B) ALA treatment decreases the number of spheres formed per well in ELDA. 33 cells seeded per well, n = 10 replicates per condition. (C) Representative images of tumor spheres derived from GBM 12-0160 and GBM 12-0106. Scale bar, 100 μm. (D) Schema depicting design of ELDAs. Assays shown in (A–C) done with concurrent ALA treatment in 96 well plates; assays shown in (E,F) done with 2 weeks ALA pretreatment followed by seeding cells in neural stem cell (NSC) medium without ALA in 96 well plates. (E) Extreme limiting dilution assays (ELDAs) show 2-week pretreatment with ALA decreases stem cell frequency in GBM cells. Stem cell frequency (1 in n) for each condition shown on plot. 33, 11, 3, 1 cells seeded per well, n = 12 replicates per condition. (F) 2-week pretreatment with ALA decreases the number of spheres formed per well in ELDA. 33 cells seeded per well, n = 10 replicates per condition. Data shown are mean +/− SEM. Data analyzed using ELDA Chi-square test (A and E), One-Way ANOVA followed by multiple t-tests (B,F); ns: not significant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001.