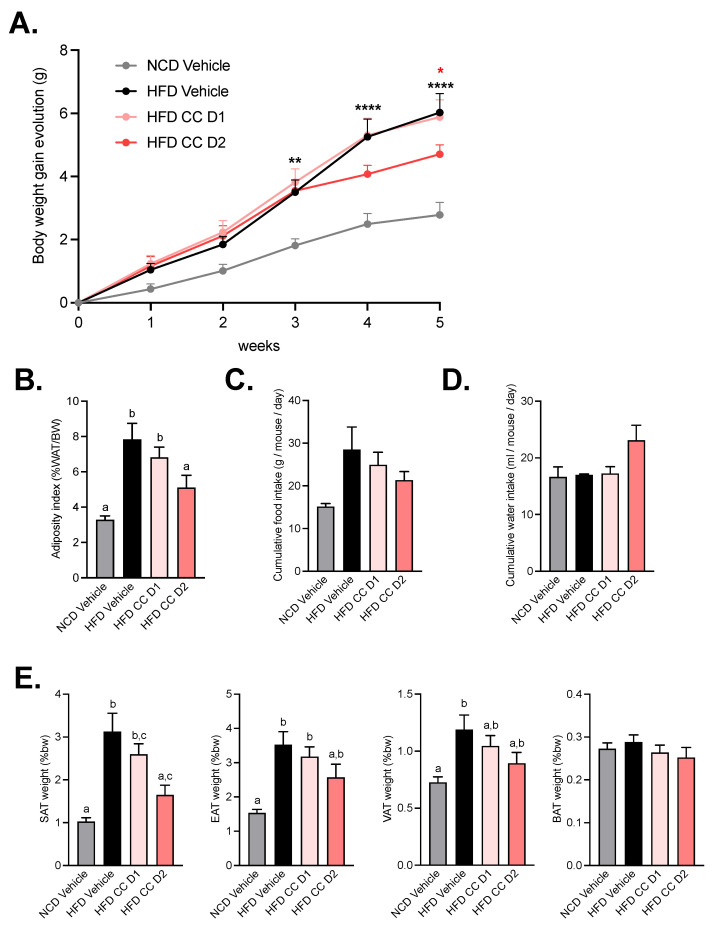
Figure 1.
Camu-Camu prevents obesity in diet-induced obese mice only at high dose of treatment. Effects of oral administration of vehicle or CCE on (A) body weight gain evolution, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 vs. HFD vehicle based on 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test, (B) adiposity index (% of total white adipose tissue mass divided by the body weight), (C) cumulative food intake, (D) cumulative water intake, (E) relative fat-mass distribution (% of body weight) of subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT), epididymal adipose tissue (EAT), visceral adipose tissue (VAT), and brown adipose tissue (BAT). Per group, n = 9–10. In figures (B,E) data with different superscript letters are significantly different (p < 0.05) according to post hoc ANOVA one-way statistical analysis (Bonferroni’s post hoc test). In panel (A), only statistics vs. HFD vehicle were presented in the graph. The significant comparisons were: ** p < 0.01 at week 3, and **** p < 0.0001 at week 4 and 5 for HFD vs. NCD vehicle. and * p < 0.05 at week 5 for HFD CCE D2 vs. HFD vehicle.