TABLE 2.
Main steps in population model building for oral dataa
| Stepb | Model | Objective functionc | Commentary |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Monocompartmental CL, V, ka | 1,016 | ς2 = 7.61 |
| 2 |
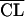 linearly related to PNA linearly related to PNA |
666 | ς2 = 0.470; PNA influences 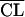
|
| 3 |
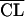 linearly related to PNA, linearly related to PNA, 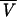 linearly related to BW linearly related to BW |
648 | ς2 = 0.291; BW influences 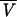
|
| 5 |
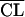 linearly related to PNA, linearly related to PNA, 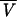 proportional to BW proportional to BW |
650 | ς2 = 0.288; 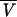 is proportional to BW is proportional to BW |
| 8 |
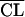 = θ1 · GFR · (BSA/1.73), GFR = (7.2 × PCAθ3)/(θ2θ3 + PCAθ3) = θ1 · GFR · (BSA/1.73), GFR = (7.2 × PCAθ3)/(θ2θ3 + PCAθ3) |
560 | ς2 = 0.219; this clearance model is better |
| 10 |
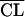 = θ1 · GFR (BSA/1.73) · (40/SCR) = θ1 · GFR (BSA/1.73) · (40/SCR) |
583 | ς2 = 0.202; scatterplots are better than those in step 8 |
| 16 | Similar to step 10, but with zero-order absorption rate | 596 | ς2 = 0.554; the fit is worse than that in step 10 |
| 17 | Bicompartmental model: 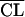 = θ1 · GFR (BSA/1.73) · (40/SCR) = θ1 · GFR (BSA/1.73) · (40/SCR) 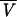 = θ2 · BW = θ2 · BW 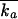 = θ3 = θ3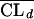 = θ4 · BW = θ4 · BW 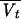 = θ5 · BW = θ5 · BW |
577 | ς2 = 0.183; not significantly better than the one-compartment model |
Abbreviations: θ1 to θ6, population parameters to be estimated; ς2, common error variance. To simplify notations, the subscript j on typical parameter values and covariates, the normalization of the covariates with respect to their median, and the ratio with F have been omitted. After step 5, 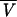 has the same definition in all remaining steps. After step 8, GFR has the same definition in all remaining steps.
has the same definition in all remaining steps. After step 8, GFR has the same definition in all remaining steps.
Some steps have been omitted for brevity.
Function to be minimized. The critical change is 3.84 for 1 degree of freedom at the 0.05 level.
