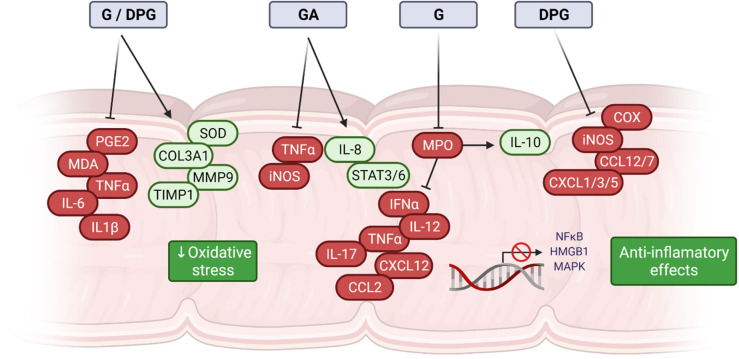
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms of Glycyrrhiza glabra-derived compounds in intestinal disorders. Compounds derived from Glycyrrhiza glabra have anti-inflammatory potential. G, GA, and DPG act through the inhibition of HMGB1, TLR4, and RAGE receptors and significantly regulate important cytokines, interleukins, and genes involved in the inflammatory process. These effects are related to the capacity of regulating important inflammatory signaling pathways such as HMGB1, NF-κB, and MAPK. Oxidative stress is significantly reduced because of cellular and molecular changes, and consequently, the inflammatory process is attenuated as a result of treatment with these compounds.